The gallbladder, a small organ tucked beneath the liver, plays a crucial role in digesting fats by storing and releasing bile. However, various disorders can disrupt its function, leading to discomfort or severe complications. In this article, we explore common gallbladder diseases, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Symptoms and Their Frequency
| Symptom | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Abdominal Pain | 85% |
| Nausea or Vomiting | 70% |
| Jaundice | 50% |
| Bloating | 65% |
| Indigestion | 40% |
This chart highlights the frequency of common symptoms associated with gallbladder diseases, with abdominal pain being the most prevalent at 85% and indigestion the least frequent at 40%.
What Is the Gallbladder and Why Is It Important?
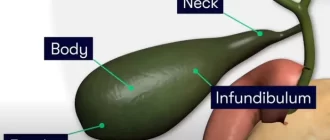
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ that stores bile produced by the liver. Bile aids in breaking down fats in the digestive system. Though small, the gallbladder’s role is significant in maintaining digestive health. Dysfunction in the gallbladder can cause significant issues, affecting digestion and overall well-being.
Common Gallbladder Diseases
- Gallstones (Cholelithiasis)
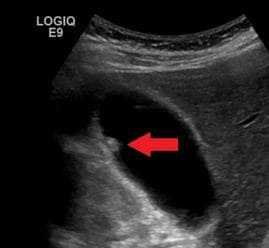
- Overview: Gallstones are solid particles that form from bile cholesterol and salts. They can block bile ducts, causing pain and inflammation. Left untreated, they may lead to severe infections or organ damage.
- U.S. Case Example: A 42-year-old woman from Texas experienced sudden abdominal pain and nausea. Ultrasound revealed multiple gallstones, prompting surgical removal of the gallbladder.
- Severity and Impact: Gallstones affect approximately 10-15% of the U.S. population, with an estimated 1 million surgeries performed annually to address this condition.
- Cholecystitis
- Overview: Inflammation of the gallbladder, often due to gallstones blocking the bile ducts.
- Symptoms: Severe pain in the upper right abdomen, fever, and nausea, resembling a “tight band” around the abdomen that intensifies with deep breaths.
- Treatment: Antibiotics, pain management, and, in severe cases, surgery. If untreated, it can escalate into a life-threatening infection or sepsis.
- Gallbladder Polyps
- Overview: Growths on the gallbladder lining, usually benign but occasionally cancerous.
- Treatment: Regular monitoring or surgical removal if polyps are large or symptomatic.
- Statistics: Polyps are detected in about 4% of imaging studies, with less than 5% showing malignancy.
- Gallbladder Cancer
- Overview: A rare but aggressive form of cancer. Early detection is critical to improving survival rates.
- Risk Factors: Gallstones, chronic inflammation, and certain genetic predispositions.
- U.S. Impact: Gallbladder cancer accounts for less than 1% of all cancer cases but has a five-year survival rate of only 19% when diagnosed late.
- Biliary Dyskinesia
- Overview: A functional disorder where the gallbladder does not empty bile properly, causing digestive disruptions.
- Symptoms: Chronic abdominal pain described as a “heaviness” or “dragging sensation,” often exacerbated by fatty meals.
- Treatment: Dietary changes or cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder).
Recognizing the Symptoms of Gallbladder Issues
Gallbladder disorders often present with overlapping symptoms. Common signs include:
- Pain in the upper right abdomen, often described as a sharp, stabbing sensation or a dull ache that worsens after fatty meals, particularly fried or rich foods.
- Nausea or vomiting, which may feel similar to motion sickness or food poisoning, leaving you unable to keep food down for hours.
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), which can be alarming as it visibly indicates bile duct blockage.
- Bloating and indigestion, manifesting as a persistent feeling of fullness, even hours after eating, coupled with frequent burping or gas.
Age Trends in Gallbladder Diseases
This chart illustrates how the prevalence of gallbladder diseases increases with age, peaking at 90% in individuals aged 60 and above. Early diagnosis and prevention are critical in older age groups.
Risk Factors for Gallbladder Diseases
Some factors increase the likelihood of developing gallbladder issues:
| Risk Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Age | Risk increases with age, especially >40. Gallstones are more common in older adults due to slowed bile flow. |
| Gender | Women are at higher risk than men, partly due to hormonal factors like estrogen, which can increase bile cholesterol levels. |
| Obesity | Excess weight raises cholesterol levels in bile, promoting gallstone formation. Those with BMI >30 are twice as likely to develop issues. |
| Diet | High-fat, low-fiber diets contribute to gallstone formation by increasing bile cholesterol saturation. A fiber-rich diet lowers this risk. |
| Genetics | Family history plays a role; individuals with a parent or sibling with gallstones have a significantly higher likelihood of developing them. |
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Common diagnostic tools include:
- Ultrasound: The primary imaging test for detecting gallstones and inflammation. Cost in the U.S.: $300–$600.
- HIDA Scan: Assesses gallbladder function. Effectiveness: 9/10. Cost: $1,200–$2,500.
- Blood Tests: Detects infection or bile duct obstruction. Cost: $50–$200 depending on panels performed.
Treatment Approaches:
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a low-fat diet and maintaining a healthy weight. Effectiveness: 6/10 for symptom management; costs are minimal if self-managed.
- Medications: To dissolve gallstones or manage inflammation. Effectiveness: 7/10; works best for small cholesterol stones. Average cost: $100–$200 per month.
- Surgical Interventions: Cholecystectomy is the standard treatment for severe or recurrent cases. Effectiveness: 10/10 for complete resolution of symptoms. Cost: $10,000–$20,000, depending on the hospital and region.
Expert Insights
Reyus Mammadli, a healthcare advisor, emphasizes: “Prevention is key. A balanced diet rich in fiber and regular physical activity significantly reduces the risk of gallbladder diseases. For those with symptoms, seeking early medical evaluation can prevent complications.”
Editorial Advice
Gallbladder diseases are common but manageable with timely intervention and lifestyle adjustments. If you experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, or jaundice, consult a healthcare provider promptly. Understanding the risks and taking preventive steps can help you maintain gallbladder health and overall well-being.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.