Pneumonia is a lung infection that can be extremely severe and result in death if not identified and treated quickly. It can impact individuals of all ages and originates from bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
In this article, we will address frequently misunderstood facts regarding pneumonia and provide helpful information for individuals experiencing symptoms or seeking to learn more about the condition.
Introduction to Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a sudden respiratory illness that can impact people at any stage of life. It develops when air sacs in the lungs become swollen, and are filled with liquid and pus. Bacteria, viruses or fungi are responsible for causing pneumonia, with the majority originating from microorganisms harboured in the upper respiratory tract.
Pneumonia is characterized by frequent coughing, fever, chills, mucous secretion, and respiratory distress. In some cases, a person may even experience confusion or chest pain along with cyanosis. It is essential to diagnose and treat pneumonia promptly to avoid severe health complications that may occur if it remains untreated.
Types of Pneumonia
Types of pneumonia are determined based on the cause of the infection.
- Bacterial pneumonia is caused by different bacteria, with the most common being Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Hospital-acquired pneumonia affects people who have been hospitalized while ventilator-associated pneumonia affects those who use ventilators.
- Viral pneumonia, on the other hand, is caused by various viruses including influenza.
- COVID-19 is another type of pneumonia caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Symptoms may vary depending on the age group, with younger children typically having higher breathing rates.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Pneumonia is a serious respiratory illness that affects the lungs.
Symptoms of pneumonia differ from person to person, but the most common ones include cough, fever, and difficulty breathing. In some cases, individuals may experience digestive symptoms like nausea and poor appetite. Infants and the elderly may experience rapid breathing or lower section signs of the disease.
If someone experiences these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
The diagnosis of pneumonia can take some time and requires testing to determine the type of bacteria or virus causing the infection. Antibiotics are the most common treatment option for bacterial pneumonia, while antiviral medication is used for viral pneumonia. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide intravenous antibiotics and oxygen therapy.
It is important to take preventative measures, such as practicing good hygiene and vaccination, to reduce the risk of contracting pneumonia. After recovering from pneumonia, it is recommended to ease back into regular activity and take measures to support lung health.
Causes
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of microbes, such as bacteria or viruses. Inflammation in the alveoli of the lungs can make it difficult for oxygen to pass through, and the cough reflex is impaired, preventing mucus and foreign matter from being expelled.
It is important to note that individuals with weakened immune systems may be more susceptible to fungal infections causing pneumonia. Taking precautions such as washing hands frequently and avoiding contact with those who are sick are critical steps in preventing the contraction of pneumonia, a potentially severe respiratory infection.
Treatment Options
Once the cause of pneumonia has been identified, treatment can begin.
Antibiotics are the most common treatment for bacterial pneumonia, as they kill the bacteria causing the infection. Antiviral medication may be used to treat viral pneumonia, which cannot be treated with antibiotics.
In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide intravenous antibiotics and oxygen therapy. If the patient is struggling to breathe, oxygen therapy can be used to keep their blood oxygen level stable.
It’s important to note that oral antibiotics can treat most cases of bacterial pneumonia, but it’s crucial to take the entire course of antibiotics, even if the patient begins to feel better. Failure to do so can increase the risk of antibiotic resistance. In the case of hospitalization, initial empirical therapy should be broad and cover the likely causative organisms.
1. Antibiotics
When it comes to treating bacterial pneumonia, antibiotics are the most common and effective treatment option. These medications work by killing the bacteria causing the infection, allowing the body’s immune system to fight off the remaining bacteria and heal.
However, it is important to note that antibiotics are not effective against viral pneumonia, which requires antiviral medication. In some cases, patients may also require oxygen therapy to help them breathe or hospitalization for more intensive treatment with intravenous antibiotics and oxygen therapy.
Proper use of antibiotics is crucial in ensuring their effectiveness, as overuse or misuse can contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. By working closely with healthcare professionals and following their prescribed treatment plan, patients with pneumonia can effectively recover and prevent future infections.
2. Antiviral medication
Antiviral medication is used to treat viral pneumonia, which cannot be treated with antibiotics. These medications work by stopping the virus from multiplying and spreading throughout the body.
Treatment may also include supportive care, such as oxygen therapy or intravenous fluids. It is important to note that antiviral medication is only effective if started early in the course of the illness.
Therefore, it is important to seek medical attention promptly if symptoms of pneumonia are present. Those with weakened immune systems, the elderly, and young children may be at higher risk for complications from viral pneumonia and may require hospitalization for treatment.
3. Oxygen therapy
When a patient with pneumonia is struggling to breathe, oxygen therapy may be necessary to stabilize their blood oxygen level.
This treatment involves providing additional oxygen through a nasal cannula, face mask, or other device. Oxygen supplementation can help the patient breathe easier and reduce the strain on their heart and lungs.
It is important to monitor the patient’s oxygen levels to avoid over-oxygenation, which can cause harm. Oxygen therapy is not without risks, but with proper monitoring and administration, it can be an effective intervention for those with respiratory conditions.
4. Hospitalization
When pneumonia is particularly serious, hospital admission may be required in order to quickly provide medical treatment.
Being hospitalized enables urgent delivery of intravenous antibiotics and oxygen therapy, which are crucial for treating severe pneumonia cases. Hospitalized patients often receive antibiotics through their veins to administer higher doses of medication and achieve more effective treatment against infections.
Oxygen treatment may also be needed for patients having difficulty breathing to maintain stable levels of blood oxygen. Furthermore, medical experts can closely observe patients who are admitted to hospitals, giving them the opportunity to make necessary modifications to their treatment on time.
Although hospitalization may not always be essential for treating pneumonia, it may become necessary in severe instances to guarantee the most favorable results for the patient.
Pneumonia and COVID-19
Pneumonia, a potentially perilous infection of the lungs, is even more alarming when coupled with COVID-19. This novel virus has the potential to cause serious breathing problems and pneumonia in certain individuals, mostly those who are elderly or have pre-existing respiratory conditions.
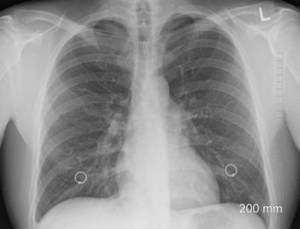
The primary CT characteristic of COVID-19-induced pneumonia is the presence of ground-glass opacities. While most people only experience mild COVID-19 symptoms, about 15% develop more serious complications like pneumonia. Laboratory findings have linked increased CRP to the severity of COVID-19 pneumonia.
There are a variety of ways to treat COVID-19 pneumonia, such as receiving oxygen therapy or being hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics and oxygen therapy, as well as taking antiviral medication. It is crucial to take steps to prevent the spread of both COVID-19 and pneumonia and lead a healthy lifestyle after recovering from it to minimize the chances of further problems.
Prevention
Prevention is key when it comes to pneumonia. The most effective way to prevent the disease is to get vaccinated against bacteria and viruses that commonly cause it. This is especially true for vulnerable populations such as young children and the elderly.
Maintaining good health habits such as eating right, exercising, and getting enough sleep can also help prevent pneumonia and other diseases. It is important to regularly wash your hands to prevent the spread of infection, especially after using the bathroom or blowing your nose.
Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke exposure is also crucial for preventing pneumonia and improving overall health.
If you do get pneumonia, it is important to seek prompt medical treatment and follow the prescribed course of antibiotics or antiviral medication.
After recovering from pneumonia, it is important to gradually resume physical activity and follow up with your healthcare provider to prevent complications or recurring infections.
How to live after pneumonia
After recovering from pneumonia, it’s important to take steps to maintain overall health and prevent relapse.
Adequate rest and hydration should continue to be a priority, as well as avoiding smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke. It’s also recommended to stay up to date on vaccinations, particularly for pneumonia and the flu.
Regular exercise can help to improve lung function and overall fitness, but it’s important to start slowly and gradually increase intensity.
Follow-up appointments with a doctor may be necessary to check lung function and ensure that recovery is progressing as expected.
Overall, taking these steps can help to ensure a healthy future after dealing with pneumonia.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.