Gallbladder polyps are growths that protrude from the inner surface of the gallbladder. They can be either true neoplastic growths or pseudopolyps of cholesterol balls clinging to the wall of the gallbladder.
Gallbladder polyps can be asymptomatic or cause symptoms of cholecystitis which include right upper abdominal discomfort, nausea, and food intolerances.
Oftentimes, polyps are discovered incidentally during routine imaging or upon pathologic examination of surgically removed gallbladders.
Causes
- Excess cholesterol deposits – Gallbladder polyps can form due to a condition called cholesterolosis. This happens when there is an abnormal accumulation of cholesterol lipids that attach to the gallbladder wall.
- Inflammation – Chronic inflammation of the gallbladder wall, known as cholecystitis, can lead to the development of inflammatory polyps.
- Abnormal cell growth – Benign tumors composed of cells that resemble the lining of the biliary tract can cause gallbladder polyps. These have a .5% risk of becoming cancerous.
- Family History – There is some evidence that family history could play a role in your risk of developing gallbladder polyps.
- Poor fat metabolism – There is also some connection between the way your body processes fat and the development of gallbladder polyps. If your gallbladder doesn’t help break down fats efficiently, you may be more likely to get polips.
Symptoms
- Nausea: Feeling queasy or sick to your stomach may be a sign of gallbladder polyps.
- Vomiting: This symptom may occur along with nausea or on its own.
- Upper abdominal pain: Pain or discomfort in the upper right part of your abdomen may indicate the presence of polyps.
- Similar symptoms for benign and cancerous polyps: There is no difference in symptoms between those with benign and cancerous polyps.
- No symptoms: It’s important to note that many people with gallbladder polyps experience no symptoms at all.
Because most people have no symptoms, gallbladder polyps are often discovered during medical exams for other conditions.
Regular monitoring is important. If you are diagnosed with gallbladder polyps, it’s important to have regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor any changes or growth.
Risk Factors
Gallbladder polyps are a relatively common health condition that affects many people worldwide. But certain factors can increase your risk of developing them, and it’s important to pay attention to them. Here are the key risk factors to keep in mind:
- Gender: Gallbladder polyps are more common in women than men.
- Age: Older people are at a higher risk of developing gallbladder polyps.
- Ethnicity: People of Mexican, Latin American, and Native American origin are more likely to develop gallbladder polyps.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases your risk of developing polyps, as well as gallstones.
- Pre-existing conditions: Having certain conditions, such as porcelain gallbladder or choledochal cysts, can increase the risk of developing polyps.
By understanding these risk factors, you can take steps to reduce your risk of developing gallbladder polyps. Consult with your doctor to learn more about how to protect your health.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of gallbladder polyps can be challenging, as the condition typically does not exhibit any clear symptoms. Often, the discovery of polyps occurs during unrelated medical exams or procedures.
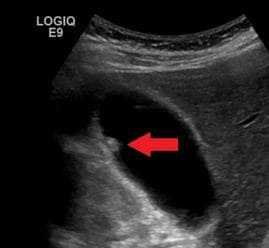
An ultrasound is the most commonly used diagnostic tool to evaluate the presence of gallbladder polyps. During the procedure, sound waves are used to produce images of the gallbladder, which allows doctors to visualize the walls and interior of the organ.
While most polyps are benign, larger polyps over half an inch in size are more likely to be cancerous. Therefore, it is essential to have regular check-ups and ultrasounds to monitor any changes and ensure proper diagnosis and management.
If cancer is suspected, additional diagnostic tests such as a biopsy or surgery may be necessary.
Treatment Options
If you have been diagnosed with gallbladder polyps, there are treatment options available. The course of treatment will depend on the size and type of polyp.
For polyps that are less than 1/2 inch in diameter and non-cancerous, your doctor may recommend regular ultrasounds to monitor the polyps for any changes.
For polyps larger than 1/2 inch in diameter or with a high probability of being malignant, cholecystectomy (surgical removal of the gallbladder) is often recommended.
In some cases, where the polyp is smaller than 10 mm, cholecystectomy may still be recommended as a preventative measure.
Along with surgical options, some natural remedies such as drinking pear juice or eating pears may help reduce the risk of gallbladder polyps.
Prevention
Pre gallbladder polyps requires maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and a balanced diet that is low in fat and high in fiber can help reduce your risk of developing gallbladder polyps.
It is essential to manage any underlying medical conditions to avoid their complications. Avoiding smoking, limiting your alcohol intake, and practicing good hygiene habits can also lower your risk of developing gallbladder polyps.
Regular monitoring and follow-up visits with your healthcare provider can help detect and diagnose polyps before they become cancerous.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing medical conditions, and regular visits with your healthcare provider can go a long way in preventing and managing gallbladder polyps.
Living with Gallbladder Polyps
Living with gallbladder polyps can be a challenge, but with the right approach, you can manage the condition effectively.
Eating a healthy diet that is low in fats and high in fiber can help minimize symptoms and prevent the condition from getting worse. Avoiding trigger foods, such as spicy or greasy meals, can also be helpful. In addition, staying active and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce your risk of complications.
It’s important to work closely with your doctor to monitor the condition and ensure that any necessary treatments are provided. By taking proactive steps to manage your gallbladder polyps, you can live a full and healthy life.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.