Cardiovascular disorders comprise a broad spectrum of diseases and conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. If left untreated, these conditions can result in potentially life-threatening complications.
Heart disease refers to a variety of conditions, such as blood vessel disease and congenital heart defects, that are frequently preventable or treatable by adopting a healthy lifestyle.
How to know if you have a cardiovascular problem? Cardiovascular diseases can affect individuals of any age, gender, race, or socioeconomic status. Heart disease is the primary cause of mortality worldwide and in the United States, with nearly half of the adult population suffering from at least one manifestation.
Individuals can effectively prevent, manage, and treat cardiovascular diseases if they have sufficient knowledge and comprehension of these issues.
Cardiovascular system morbidity statistics
| Type of Cardiovascular Disease | Description | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Coronary artery disease | Blocked or narrowed blood vessels that supply the heart | 18.2 million cases per year |
| Stroke | Blood supply to the brain is cut off, resulting in brain damage | 17.3 million cases per year |
| Hypertension | High blood pressure, which puts strain on the heart and blood vessels | 1.13 billion cases worldwide |
| Heart failure | The heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs | 26 million cases worldwide |
| Atrial fibrillation | Irregular and often rapid heart rate, which increases the risk of stroke | 37 million cases worldwide |
| Cardiomyopathy | The heart muscle becomes enlarged, thick, or rigid, impairing its ability to pump blood | 2.5 million cases per year |
| Peripheral artery disease | Narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the limbs, usually the legs | 202 million cases worldwide |
| Pulmonary embolism | Blood vessel in the lung is blocked by a blood clot, which can be fatal | 1 million cases per year |
| Aortic aneurysm | Abnormal bulging in the aorta, the largest artery in the body, which can rupture and cause bleeding | 200,000 cases per year |
Understanding Different Types of Cardiovascular Diseases
These conditions can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, leading to life-threatening complications and even mortality. The following are some of the most prevalent cardiovascular diseases:
- When blood flow to the heart muscle is restricted, coronary heart disease occurs. It can cause chest discomfort, heart attacks, and heart failure.
- Stroke and Transient Ischaemic Attack (TIA): characterized by the interruption of blood flow to the brain, resulting in brain injury or even mortality in extreme cases.
- Peripheral arterial disease is characterized by obstructions in the arteries of the extremities, frequently causing leg pain, paralysis, and persistent ulceration.
- A group of conditions that affect the aorta, the main arterial vessel in the body. A common example is an aortic aneurysm, which is characterized by a compromised, distended aorta with the potential to rupture and cause life-threatening hemorrhage.
Understanding these diseases assists in identifying risk factors, adopting a healthier lifestyle, and seeking necessary treatment.
Common Causes
- This prevalent cause of cardiovascular disease is atherosclerosis, which narrows the arteries and restricts blood flow to the heart and other organs due to the accumulation of plaque.
- A high-sodium, high-sugar, and high-fat diet, coupled with physical inactivity and smoking, can substantially increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
- Elevated blood pressure is a significant risk factor because it places additional strain on the heart and blood vessels, resulting in their deterioration over time.
- Elevated cholesterol can contribute to atherosclerosis and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- A history of heart disease in the family can predispose individuals to cardiovascular problems.
- Age and gender can both contribute to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Chronic inflammatory or autoimmune conditions can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease by causing inflammation in the blood vessels.
- Certain medications and recreational substance abuse can have a negative impact on cardiac health and contribute to the development of cardiovascular problems.
Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Diseases
- Age, ethnicity, and family history are uncontrollable risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD).
- Modifiable risk factors include smoking, diet, exercise, and other lifestyle behaviors that, when properly managed, can reduce the likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease.
- Having first-degree relatives with CVD at a relatively young age can increase the risk of developing the disease.
- Socioeconomic status: Due to limited access to nutritionally balanced diets, people with a low socioeconomic status often have a higher risk of developing CVD.
- High LDL cholesterol levels: Increased levels of “bad” cholesterol can lead to the accumulation of fatty substances in the arteries, which contributes to a variety of CVDs.
- Other health conditions, such as hypertension, obesity, and diabetes, can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Women tend to develop cardiovascular disease (CVD) at a later age than males, which may be due to hormonal alterations after menopause.
Remember that the presence of risk factors does not ensure the development of cardiovascular disease, but it does increase the likelihood of their occurrence. A healthful lifestyle can aid in mitigating these hazards.
Symptoms of Cardiovascular Diseases
- Pain, rigidity, pressure, and distress in the chest (angina) are typical symptoms of coronary artery disease.
- Cardiovascular disease is more likely to affect women who experience shortness of breath, vertigo, and extreme fatigue.
- Agony, paralysis, weakness, or chill in the legs or arms: Indicator of constricted blood vessels in these areas of the body.
- Thoracic pressure, heaviness, or discomfort: Often described as a girdle or weight around the chest.
- Agony or cramping in the legs while walking: a sign of clogged blood vessels.
- Numbness in the face or a limb, vision problems, and difficulty walking or speaking may indicate a problem with the brain’s blood vessels.
Recognizing these symptoms early may aid in the early detection of cardiovascular issues, allowing for more effective treatment options.
Importance of Early Detection and Diagnosis
The significance of early cardiovascular disease detection and diagnosis cannot be emphasized. Not only does it increase the patient’s chances of survival, but it also helps reduce the costs associated with advanced disease stages. According to the American Heart Association, cardiovascular disease (CVD) is largely preventable through early detection and a heart-healthy lifestyle.
Early detection permits opportune interventions, thereby delaying the progression of the disease and possibly preventing significant complications such as heart attacks and strokes.
Innovative technologies enable the detection of early cardiovascular disease in asymptomatic individuals, resulting in more accurate disease prognoses.
The WHO initiative aimed at the early detection and management of cardiovascular diseases emphasizes the need for both physicians and patients to prioritize heart health and disease prevention.
In conclusion, early detection and diagnosis play a crucial role in the management and prevention of cardiovascular diseases, ultimately resulting in improved health outcomes and lower healthcare costs.
Physical and diagnostic tests
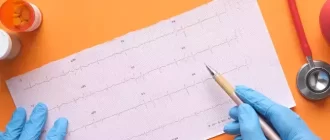
Physical and diagnostic exams are essential for identifying cardiovascular issues and determining the most effective treatment. Various tests, including non-invasive and invasive procedures, are used for this purpose. Typical diagnostic procedures include:
- Blood tests: These help assess cholesterol levels (LDL and HDL), C-reactive protein (CRP), and homocysteine, which are vital indicators of heart health.
- Electrocardiogram (EKG): This test records the electrical activity of the heart in order to detect any abnormalities or irregularities.
- Echocardiogram (echo): This test generates images of the heart using ultrasound technology to evaluate its structure and function.
- Stress testing: This evaluates the heart’s performance under physical duress, whether induced by exercise or medication.
When combined with personal and family medical histories, these tests provide a comprehensive assessment of a person’s cardiovascular health and risk factors.
Treatment Options for Cardiovascular Diseases
- Changes in Lifestyle: Adopting healthful behaviors such as a low-fat, low-sodium diet, regular exercise, adequate rest, and ceasing smoking can substantially improve cardiac health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Depending on the form of heart disease, different medications may be prescribed to treat symptoms and prevent complications. Common cardiovascular disease treatments include statins, beta-blockers, and anticoagulants.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: This individualized exercise and education program can enhance cardiac health following heart surgery. It facilitates the incorporation of a heart-healthy diet, stress management, and physical activity into daily life.
- In some instances, cardiac diseases may necessitate surgical interventions such as angioplasty, stent placement, or bypass surgery to restore blood flow and prevent further complications.
- Reducing emotional tension through practices such as mindfulness, connecting with support groups, and managing anxiety or depression can play an essential role in the management of cardiovascular diseases.
Lifestyle Modifications to Manage Cardiovascular Diseases
Modifications to one’s lifestyle are crucial for the management and prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Including healthful behaviors in your daily routine can significantly reduce the risk of developing these conditions. Here are several important lifestyle modifications that can make a difference:
- The Surgeon General recommends 2 hours and 30 minutes per week of moderate-intensity exercise, such as leisurely walking or bicycling, for adults, and 1 hour of physical activity per day for children and adolescents.
- Consume more fresh fruits and vegetables and fewer foods high in saturated fat, trans fat, and sodium to maintain a healthy diet. This will aid in maintaining normal blood pressure, cholesterol, and glucose levels.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Those who are overweight or obese are at a greater risk for cardiac disease. Maintain an appropriate weight range to reduce this risk.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption. Smoking raises your risk for heart disease, so ceasing will reduce your risk if you are a smoker. As for the use of alcohol, it should be abandoned in any case.
- Manage existing medical conditions effectively: If you have high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or diabetes, engage with your healthcare team to reduce your risk of heart disease.
By making these changes to your lifestyle, you can significantly reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease and live a healthier existence.
Dietary Changes and Nutritional Requirements
Understanding the connection between diet and cardiovascular disease is crucial for identifying cardiovascular problems. To prevent and treat cardiac disease, it is essential to implement the following dietary modifications and nutritional needs:
- Eat a diet abundant in fruits, vegetables, whole cereals, seeds, and legumes
- Consume moderate amounts of low-fat dairy products and seafood
- Reduce your consumption of processed meats, sugar-sweetened beverages, refined grains, and sodium
- Substitute olive or canola oil for saturated lipids as a healthier alternative
- Limit cholesterol consumption; individuals with elevated LDL cholesterol should consume no more than seven eggs per week.
- Contemplate supplementation in consultation with a physician.
The implementation of these modifications not only reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease, but also improves overall health and well-being.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary artery disease and peripheral artery disease, are a major health concern because they are the primary cause of mortality not only in the United States, but globally as well. To prevent the onset of such diseases, it is essential to address risk factors such as inadequate diet, substance abuse, and chronic inflammatory conditions.
Through physical examinations and diagnostic tests, early detection and diagnosis can help manage and treat these conditions more effectively. By modifying one’s lifestyle and taking prescribed medications, it is possible to substantially reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases and enhance one’s overall health.
As we continue to deal with the ever-changing landscape of the healthcare industry, it is crucial for medical professionals to stay abreast of the most recent trends and data in order to provide the best possible care for patients with cardiovascular issues. Remember that early diagnosis and treatment can save lives.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.