Hypovitaminosis E develops either by insufficient intake of this vitamin in the body or by impaired absorption.
Understanding of Vitamin E
“Beauty vitamin”, “antioxidant”, “rejuvenates” – all these people hear about vitamin E and, as a consequence, take drugs and supplements, guided by the principle “it won’t get worse. Nutritionist Tatiana Bocharova believes that this is not very rational and that it is better to spend money on quality products.
Vitamin E (or tocopherol) is one of the main antioxidants, which is involved in all metabolic processes: in particular, it ensures heart health, slows down aging and supports the balance of cholesterol in the blood. Among its other “areas of responsibility” are the proper development of muscles, the synthesis of protein and collagen, and for this reason vitamin E is actively used in cosmetology.
It is not difficult to compensate for vitamin E deficiencies. The daily requirement of vitamin E is quite small: only 15 mg for adults. For nursing mothers, it is slightly higher – 19 mg. Thus, a healthy person has no problem getting vitamin E from food.
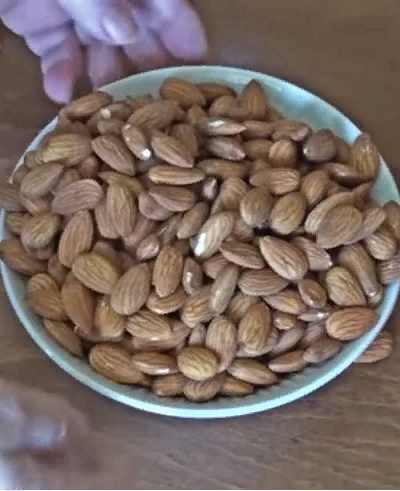
Its source can be, first, vegetable oil (44 mg per 100 g), one tablespoon of which closes the daily rate of tocopherol; secondly, almonds (25 mg per 100 g) – two handfuls of it are also equivalent to the daily requirement. Third, a useful product is sunflower seeds, 100 grams of which contain 35 milligrams of vitamin E. In addition, foods high in vitamin E include hazelnuts (21 mg), peanuts (ten milligrams) and olive oil (12 mg).
Vitamin E deficiency can occur if there are stomach or intestinal problems, such as colitis and ulcerative colitis, or gallbladder problems such as the presence of stones or missing gallbladder after surgery. However, in such a case, not only tocopherol itself, but also other vitamins and minerals will be poorly absorbed. It is necessary to consult a doctor to pick up vitamins and medicines and adjust the diet.
Useful benefits of vitamin E
- Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant;
- slows the aging process of cells and improves their nutrition;
- stimulates the immune system, participates in the protection against viral and bacterial infections;
- Improves tissue regeneration;
- stimulates capillary formation and improves vascular tone, permeability;
- Improves blood circulation;
- Protects the skin from ultraviolet rays;
- Participates in the synthesis of hormones;
- Reduces the formation of scars on the skin;
- protects against bladder cancer;
- protects against prostate cancer and Alzheimer’s disease;
- reduces body fatigue;
- helps lower blood sugar;
- Helps normal muscle function.
Vitamin E has a special positive effect on pregnancy and the reproductive system.
Health hazards of vitamin E
Vitamin E does not have harmful toxic properties, so if a small excess in the body no adverse effects are observed (calorizator). However, if the permissible rate of the vitamin is greatly exceeded, it can have a negative effect on health.
Signs of vitamin E overdose: diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, increased blood pressure, allergic reactions.
Vitamin E absorption
Pharmacokinetics: when taken orally it is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, most of it enters the lymph, quickly distributed to all tissues, slowly excreted with the bile and as metabolites in the urine.
Symptoms of Vitamin E Deficiency
The very first symptom of vitamin E deficiency is muscle hypotension and weakness. Children suffering from hypovitaminosis E are stunted in growth and weight. In addition, in infants, a lack of this vitamin can cause rickets and seborrheic dermatitis. Premature infants with hypovitaminosis E may develop retinopathy of prematurity.
A lack of tocopherol causes hemolysis (destruction, decay) of red blood cells and hemolytic anemia develops.
Lack of vitamin E contributes to the destruction of nerve fibers. And this leads to poor coordination and decreased skin sensitivity.
In women, the lack of this vitamin can cause menstrual irregularities and pregnancy failure. In men with hypovitaminosis E weakened potency.
Vitamin E promotes the absorption of vitamin A, and when it is insufficient, hypovitaminosis A develops, which is manifested by dry skin, impaired twilight, hair loss and frequent infections.
What is vitamin E
Tocopherol (vitamin E) was isolated in the 1920s. Then scientists found that without this substance normal pregnancy is impossible. Therefore, and called this substance tokopherol (tokos – offspring, phero – to bring). In 1936, Bishop and Evans obtained the first preparation of tocopherol from wheat sprouts. And in 1938, the first synthetic tocopherol appeared.
Subsequently, scientists found out that tocopherol is useful not only during pregnancy. It turned out that this substance improves blood circulation, provides its normal coagulation, participates in tissue regeneration, takes part in the formation of collagen and elastic fibers, improves skin condition, enhances immunity, provides normal muscle function. In 1997, it was found that this vitamin alleviates the course of Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes.
Nowadays, the name “vitamin E” refers to a group of 8 tocopherols. They are light yellow transparent viscous oils that break down under the influence of ultraviolet light. With food, tocopherols are absorbed in the intestines, reaching the lymph and blood. With the blood they enter the liver, where they bind to proteins and enter the blood as part of very low density lipoproteins (VLDL), where there is an exchange of tocopherol between LDL and low density lipoproteins (LDL). As part of LDL, tocopherol enters fat, muscle and nerve tissue, where it performs its functions – protects cell membranes from oxidative damage, controls the synthesis of nucleic acids and heme (an iron compound that is part of hemoglobin), optimizes cellular oxygen consumption. Non-absorbed tocopherols are excreted with the feces.
The amount of vitamin E is measured in international units (IU). Children during the first year of life need about 3-5 IU of tocopherol per day, children 1-3 years old need about 6 IU, 4-10 years old need 7 IU. Adult men need at least 10 IU of vitamin E per day, and women 8 IU. However, during pregnancy the rate increases to 10 IU, and during lactation to 12 IU. It is believed that up to 100 IU of vitamin E can be consumed without unpleasant consequences.
Hypovitaminosis can occur either when too little vitamin E is ingested with food (primary deficiency) or when for some reason it is not absorbed in the gut (secondary deficiency). Primary deficiency can occur with an improper, irrational diet. This often happens when babies are fed artificially.
Secondary insufficiency develops with any pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. These can be cystic fibrosis, malabsorption syndrome, chronic pancreatitis, short gut syndrome (when tocopherol is not absorbed because the intestine was shortened during an operation), abetolipoproteinemia (a genetic disease in which the transport and absorption of fats is impaired). Hypovitaminosis E can develop as a consequence of worm infestations, infectious diseases, hypoparathyroidism, carcinoid syndrome (condition caused by the release of hormones by tumor cells).
Diagnosis
If hypovitaminosis E is suspected, you should see a general practitioner or nutritionist. Diagnosis requires an interview with the patient, analysis of plasma levels of tocopherol.
Treatment
Treatment of vitamin E deficiency consists of prescribing tocopherol preparations and adjusting the diet. Sufferer hypovitaminosis E should eat more peas, corn, oatmeal, buckwheat, shrimp, squid. Tocopherol is also found in mackerel, zander, and eggs. Lots of vitamin E in oils – soybean, corn, sunflower, cotton and butter. Nuts, wheat germ, cabbage and lettuce are rich in this vitamin.
Secondary vitamin E deficiency should, if possible, eliminate the primary disease.
What to eat when the body is deficient in vitamin E
Foods rich in vitamin E:
- Vegetable oil
- Almonds
- Pine nuts
- Broccoli
- Mango
- Sunflower seeds
- Avocado
- Peanut paste
- Atlantic Salmon
- Sweet bell pepper
Vegetable oil
Vegetable oil is rich in vitamin E. Wheat germ oil is particularly rich in it: one tablespoon of the product covers 135% of the daily requirement of tocopherol. In addition, it lowers cholesterol levels, normalizes metabolism and strengthens the nervous system.
However, such oil is not recommended for people with cholelithiasis or urolithiasis. Replace it with sunflower or hazelnut oil – add a spoonful of any of them to a salad or sauce to make up for a third of the daily requirement for vitamin E.
Almonds
This nut can be eaten pure or added to a variety of dishes. Or try diversifying your diet with an alternative milk, butter, or almond flour. It contains 26 mg of tocopherol in 100 grams. In addition, it is a valuable source of omega-3, protein, calcium and fiber. And the included fatty acids in almonds provide easy and quick absorption of vitamin E.
Nutritionists advise eating almond kernels along with the brown skin. It has the highest concentration of antioxidants – flavonoids.
Pine nuts
Like almonds, pine nuts are an excellent source of tocopherol. One handful contains 2.7 mg of vitamin E, which covers 18% of the daily requirement. In addition, these nuts are rich in magnesium and phosphorus: these minerals strengthen bones, ensure energy metabolism and improve performance.
Cedar also has a lot of vitamin A. It is fat-soluble, so it combines well with tocopherol. And yet you should not abuse these nuts: they have a high caloric value. It is better to add a little bit of cedar to pasta and porridge.
Broccoli
Broccoli is considered one of the best natural detoxifiers. It removes toxins, excess sugar, cholesterol and carcinogens from the body. Broccoli is also high in vitamin E, and 100 grams of it fills up 10 percent of the daily dose of tocopherol.
It can also be eaten raw, but after gentle heat treatment cabbage becomes even more useful [2], [3]. Steam broccoli for no more than 5 to 10 minutes to boost your body’s vitamin content.
Mango
Not all fruits can boast high levels of vitamin E, but not mangoes. Half a fruit contains 1.5 mg of tocopherol. This is 10% of the daily rate. The juicy and flavorful tropical fruit can be found in almost any supermarket. Choosing a mango, be sure to pay attention to the condition of the skin. It should not be damaged in any way. But do not press on the fruit, as this causes unripe fruits to be damaged and begin to rot.
Sunflower seeds
Only 43 grams of sunflower seeds make up for one day’s vitamin E deficiency. Although they contain no harmful cholesterol, sunflower seeds are almost 80 percent fat and are very nutritious. To get the most out of them, nutritionists advise to take raw, unpeeled seeds. Without the shell, they are worse for storage, and during frying they lose vitamins and become a source of “empty” calories.
Avocados
Supplement your meal with half a medium avocado to make up for 14% of your daily tocopherol intake and keep you full for longer. The fruit can be added to a salad, spread on toast, turned into a sauce, or made into a sweet cream. Or simply cut an avocado in half, remove the pit, drizzle with lemon juice, salt and sprinkle with freshly ground black pepper. Although avocados are high in fat, studies show that including them in your diet can help you consume fewer calories and help you lose weight.
Peanut Paste
Peanut butter is not just a treat, but also a balanced source of energy. The product consists of 25% easily digestible protein and only 20% carbohydrates. This makes it possible to consume peanut butter during periods of maintaining a low-carbohydrate diet. In addition, it is rich in tocopherol: 100 g of the product covers 45% of the daily norm of the vitamin. By the way, to prepare such a paste yourself is not difficult: crush the peanuts in a blender for 10-15 minutes. If desired, add salt, honey or bitter chocolate.
Atlantic Salmon
Salmon is packed with the “vitamin of youth.” A 200-gram steak provides 16% of your daily requirement for tocopherol. Salmon is also one of the leaders in the amount of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Our body cannot synthesize them on its own. In deficiency of these substances our hair becomes dull and dry and our skin becomes thin. But keep in mind: salmon is not suitable for frequent consumption. It accumulates toxic substances from the environment. Doctors advise to eat this fish not more than twice a week.
Bell peppers
Just one medium sweet bell pepper covers 13 percent of the daily value of vitamin E. They also contain a daily dose of the rare vitamin P, which strengthens the walls of blood vessels. And for the amount of ascorbic acid, this vegetable surpasses oranges and lemons.
If you add bell peppers to your daily diet, you can restore the microflora of the intestines, lower blood pressure, strengthen immunity. Choosing a vegetable, look carefully at the skin of the fruit. The less damage and dents on it – the better vitamins are preserved.
Prevention
To prevent hypovitaminosis E healthy people need only a proper diet.
Babies born at term do not need to be prescribed vitamin E additionally, however, premature babies need this vitamin in most cases.
Important to know: expert comment
Vitamin E is necessary and important: it is involved in many processes in the human body. However, prolonged intake in high doses can lead to hypervitaminosis. An excess of vitamin E is accompanied by headache, dizziness, increased fatigue, abdominal pain, visual impairment. During pregnancy, vitamin E, as well as other drugs, is used only on the doctor’s recommendation.
If prolonged use of vitamin E, be aware of the possible effect of the drug on the absorption of other vitamins and minerals. It has been found that vitamin E increases the bioavailability and absorption of vitamins A and C and selenium. At the same time, it reduces the absorption of iron, which is especially important for patients suffering from iron deficiency anemia. In addition, with caution should take the vitamin people who are on therapy with anticoagulants (warfarin) and cytostatics (cyclosporine). Tocopherol may affect their effects.
Vitamin E is destroyed by sunlight, so store products in a place where light does not penetrate. Of all the vitamins, tocopherol is the least sensitive to heat treatment. Still, it is desirable to reduce cooking time and to use gentle methods of food processing. For example, steaming, baking in the oven or stewing. Most tocopherol is contained in cold-pressed oils, so it is recommended to add them when preparing salads.
Because of its properties, vitamin E is widely used in cosmetology. It is included in various cosmetic products: serums, oils, creams, emulsions, balms. Tocopherol is a mandatory component of products for the care of sensitive and irritated skin, shampoos and hair masks, medicinal nail polish. It is not accidentally called the “vitamin of youth”: tocopherol is used in lines of anti-aging cosmetics, as well as in preparations for the prevention and correction of age-related skin changes.
Vitamin E softens the skin, thus increasing its elasticity and turgor. It is effective against pigmentation, which is why it is often included in whitening products. In addition, tocopherol helps to restore the epidermal barrier – it is used for burns, dry skin. Another useful property of this vitamin: it protects the skin from the negative effects of the external environment and is included in various protective creams and lip sticks against frost.
Conclusion
The main function of vitamin E in the body is antioxidant: inhibition of peroxidation of unsaturated fatty acids by capturing the unpaired electrons of active oxygen radicals. It was found that due to this property tocopherol prevents rancidity of oil, and in humans protects cell membranes from the action of free radicals. They are formed constantly, and their production increases with smoking, various diseases. Thus, cells constantly need protection from oxidation, and if there is a lack of antioxidants, their membranes will be destroyed. Other functions of vitamin E include participation in the formation of hemoglobin, in gene expression, as well as reducing the production of prostacyclins by endothelial cells and thromboxanes by platelets, which prevents platelets from attaching to the inner lining of blood vessels and reduces the risk of atherosclerosis and thrombosis.
Causes of vitamin E deficiency can vary. Its insufficient intake with food is quite rare, unless a person is starving. Bile is necessary for normal absorption of vitamin E, so hypovitaminosis is due to impaired absorption of fats in the intestine – malabsorption syndrome (in celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, premature or low birth weight infants), insufficient bile formation or flow into the intestine (due to malformation). In addition, a decrease in certain proteins in the blood transport of vitamin E to organs and tissues is impaired, which also leads to its deficiency (e.g., in hereditary abetalipoproteinemia).
When tocopherol deficiency affects the whole organism, but primarily tissues with large membrane length and high intensity of oxidation processes, i.e. muscle and nerve, tissues with a high degree of proliferation (epithelium of male glands, liver and kidneys, germ tissue), as well as red blood cells, which can be destroyed by tocopherol deficiency.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.