Gout is defined by painful joint inflammation, often in the first metatarsophalangeal joint, resulting from precipitation of monosodium urate crystals in a joint area. Gout is typically detected utilizing clinical criteria from the American College of Rheumatology.
Diet
What foods should you eat?
Although a gout-friendly diet eliminates lots of foods, there are still lots of low-purine foods you can delight in.
Foods are thought about low-purine when they have less than 100 mg of purines per 3.5 ounces (100 grams).
Here are some low-purine foods that are typically safe for individuals with gout:
- Fruits: All fruits are generally very good for gout. Cherries might even help avoid attacks by decreasing uric acid levels and minimizing inflammation.
- Veggies: All vegetables are fine, including potatoes, peas, mushrooms, eggplants, and dark green leafy veggies.
- Legumes: All legumes are excellent, including lentils, beans, soybeans, and tofu.
- Nuts: All nuts and seeds.
- Whole grains: These include oats, brown rice, and barley.
- Dairy items: All dairy is safe, however, low-fat dairy appears to be specifically helpful.
- Eggs
- Drinks: Coffee, tea and green tea.
- Herbs and spices: All herbs and spices.
- Plant-based oils: Including canola, coconut, olive and flax oils.
Foods you can eat in moderation
Aside from organ meats, game meats, and specific fish, most meats can be consumed in small amounts. You ought to restrict yourself to 4– 6 ounces (115– 170 grams) of these a few times each week.
They include a moderate amount of purines, which is thought about to be 100– 200 mg per 100 grams. Thus, consuming too much of them might activate a gout attack.
Meats: These include chicken, beef, pork, and lamb.
Other fish: Fresh or canned salmon generally consists of lower levels of purines than a lot of other fish.
Foods you ought to eat with gout consist of all vegetables and fruits, entire grains, low-fat dairy items, eggs and a lot of beverages. Limitation your usage of non-organ meats and fish like salmon to portions of 4– 6 ounces (115 – 170 grams) a couple of times weekly.
Sample menu to prevent gout
Here’s what you may eat throughout a typical day on a gout diet.
Breakfast
- Whole-grain, unsweetened cereal with skim or low-fat milk
- 1 cup fresh strawberries
- Coffee
- Water
Lunch
- Roasted chicken breast slices (2 ounces) on a whole-grain roll with mustard
- Blended green salad with vegetables, 1 tablespoon nuts, and balsamic vinegar and olive oil dressing
- Skim or low-fat milk or water
Afternoon snack
- 1 cup fresh cherries
- Water
Dinner
- Roasted salmon (3 to 4 ounces).
- Roasted or steamed green beans.
- 1/2 to 1 cup whole-grain pasta with olive oil and lemon pepper.
- Water.
- Low-fat yogurt.
- 1 cup of fresh melon.
- Caffeine-free beverage, such as natural tea.
Medications
Medications to treat gout attacks
Drugs used to deal with acute attacks and avoid future attacks include:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs include non-prescription alternatives such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve), along with more-powerful prescription NSAIDs such as indomethacin (Indocin) or celecoxib (Celebrex).
Your doctor might prescribe a higher dose to stop an acute attack, followed by a lower everyday dose to prevent future attacks.
NSAIDs bring dangers of stomach pain, bleeding, and ulcers.
Colchicine. Your physician may recommend colchicine (Colcrys, Mitigare), a type of painkiller that efficiently minimizes gout pain. The drug’s effectiveness may be offset, however, by side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, specifically if taken in large doses.
After an acute gout attack fixes, your medical professional may recommend a low everyday dose of colchicine to avoid future attacks.
Corticosteroids. Corticosteroid medications, such as the drug prednisone, may manage gout inflammation and pain. Corticosteroids might be in pill form, or they can be injected into your joint.
Corticosteroids are typically utilized just in people with gout who can’t take either NSAIDs or colchicine. Side effects of corticosteroids may consist of mood changes, increased blood sugar level levels and raised blood pressure.
Medications to prevent gout
If you experience numerous gout attacks each year, or if your gout attacks are less regular but particularly painful, your physician may advise medication to reduce your danger of gout-related problems. If you currently have proof of damage from gout on joint X-rays, or you have tophi, chronic kidney disease or kidney stones, medications to lower your body’s level of uric acid might be suggested. Options consist of:
Medications that obstruct uric acid production. Drugs called xanthine oxidase inhibitors (XOIs), including allopurinol (Aloprim, Lopurin, Zyloprim) and febuxostat (Uloric), limit the amount of uric acid your body makes. This might reduce your blood’s uric acid level and decrease your threat of gout.
Side effects of allopurinol consist of a rash and low blood counts. Febuxostat side effects include rash, nausea, lowered liver function and an increased risk of heart-related death.
Medication that improves uric acid removal. These drugs, called uricosurics, include probenecid (Probalan) and lesinurad (Zurampic). Uricosuric drugs enhance your kidneys’ capability to get rid of uric acid from your body. This may reduce your uric acid levels and lower your threat of gout, but the level of uric acid in your urine is increased. Side effects include a rash, stomach pain, and kidney stones. Lesinurad can be taken just along with an XOI.
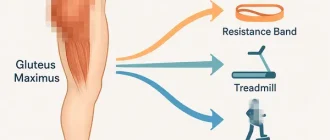
Exercises
Do workouts often. Remaining physically active becomes part of a healthy way of life, and it may assist avoid a future gout attack. Among the lots of advantages of working out with gout, it helps you lose weight (if you require to). Being overweight or obese is a danger element for gout, however, if you currently have gout, keeping a healthy weight may assist avoid a gout attack. A workout can likewise help you successfully manage stress.
If you’re presently experiencing a gout attack, you shouldn’t work out until your pain and inflammation are lowered.
If you’re new to exercise or have not worked out in a long period, talk to your physician about how to be active. If you establish new symptoms when exercising, let him, or her learn about them.
Exercises and Gout Pain
When gout is actively triggering inflammation in a joint (arthritis), all efforts need to be directed toward eradicating the inflammation. This typically suggests resting the joint, ice/cold applications, and anti-inflammatory medications.
Exercising a joint that is currently inflamed can extend the inflammation and trigger more pain. Gently moving the joint through its variety of motion can in some cases avoid stiffness.
After the inflammation of the joint has actually silenced down, regular workout is often encouraged to re-establish strength and movement of the muscles around the joint.
The workout has no benefit or effect on breaking up small crystals of gout (monosodium urate crystals) in the joints. These tiny (microscopic) crystals are only as long as a white blood cell is broad. They dissolve (vanish) and type according to the body’s metabolic process (processing of substances), state of hydration (quantity of water), and in response to medications that influence the uric acid level in the blood.
What Else You Should Know about Gout?
Diagnosis might be confirmed by recognition of monosodium urate crystals in synovial fluid of the impacted joint. Acute gout may be treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, or colchicine. To minimize the likelihood of persistent flares, patients must restrict their consumption of specific purine-rich foods (e.g., organ meats, shellfish) and avoid alcoholic drinks (specifically beer) and beverages sweetened with high-fructose corn syrup.
Intake of vegetables and low-fat or nonfat dairy items need to be encouraged. The use of loop and thiazide diuretics can increase uric acid levels, whereas making use of the angiotensin receptor blocker losartan increases urinary excretion of uric acid. A decrease of uric acid levels is crucial to preventing gout flares.
Allopurinol and febuxostat are first-line medications for the avoidance of persistent gout, and colchicine and/or probenecid are reserved for patients who can not tolerate first-line agents or in whom first-line representatives are ineffective. Patients getting urate-lowering medications must be treated concurrently with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine, or low-dose corticosteroids to avoid flares.
Treatment needs to continue for at least 3 months after uric acid levels fall below the target objective in those without tophi, and for 6 months in those with a history of tophi.
Gout is the most typical inflammatory arthropathy, affecting more than 8 million Americans. Gout accounts for approximately 7 million ambulatories see in the United States each year at the cost of almost $1 billion. Threat elements consist of genes, age, sex, and diet. These elements might contribute to a high serum uric acid level, which is presently specified as a value of at least 6.8 mg per dL (405 μmol per L).
Other Tips to Prevent a Gout
Serum urate — reducing treatment should be started to prevent recurrences personality with a history of gout and any one of the following: a minimum of two flares annually (one annually personally with chronic kidney disease stage 2 or higher), tophi, or a history of nephrolithiasis.
Serum urate needs to be reduced to a target of less than 5 to 6 mg per dL (297 to 357 μmol per L), depending upon the crystal and tophaceous burden. Normal serum urate levels do not exclude the medical diagnosis of gout. They must be kept track of periodically to examine preventive therapy in patients with reoccurring gout and a history of raised urate levels. Urate-lowering treatment needs to be continued for 3 to six months after a flare if there are no ongoing symptoms. Treatment should continue forever if there are continuous signs or symptoms (e.g., one or more tophi on evaluation).
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.