Treatment of inflamed hemorrhoids should not be delayed, because it can only aggravate an already unpleasant disease. If you are faced with hemorrhoids, then you do not need to explain what kind of discomfort and pain it is. Inflamed hemorrhoids are especially painful for the patient, so it is especially important to know how to treat it.
What Is Inflamed Hemorrhoid?
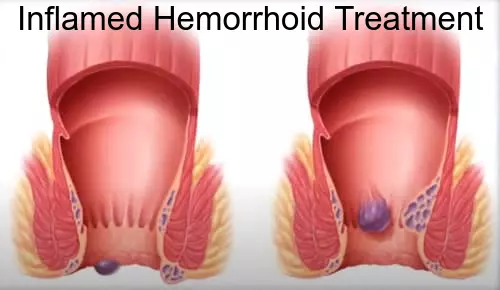
Hemorrhoids (HEM-uh-roids), also called piles, are swollen veins in your anus and lower anus, similar to varicose veins. Hemorrhoids can develop inside the anus (internal hemorrhoids) or under the skin around the anus (external hemorrhoids).
Almost three out of 4 adults will have hemorrhoids from time to time. Hemorrhoids have a number of causes, but frequently the cause is unidentified.
Fortunately, effective alternatives are readily available to deal with inflamed hemorrhoids. Many individuals get relief with home treatments and lifestyle changes.
Inflamed Hemorrhoids Signs and Types
Symptoms and signs of inflamed hemorrhoids generally depend upon the type of hemorrhoid.
External hemorrhoids
These are under the skin around your anus. Symptoms and signs might include:
- Itching or inflammation in your anal area
- Pain or discomfort
- Swelling around your rectum
- Bleeding
Internal hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids lie inside the rectum. You usually can’t see or feel them, and they rarely trigger discomfort. However straining or inflammation when passing stool can cause:
- Pain-free bleeding during bowel movements. You might notice percentages of bright red blood on your toilet tissue or in the toilet.
A hemorrhoid to push through the anal opening (prolapsed or extending hemorrhoid), resulting in pain and inflammation.
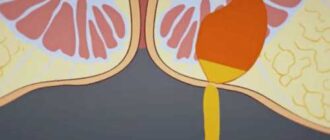
Thrombosed hemorrhoids
If blood pools in an external hemorrhoid and forms an embolism (thrombus), it can result in:
- Severe pain
- Swelling
- Inflammation
- A hard lump near your rectum
Treatment for Inflamed Hemorrhoid
Home remedies
You can frequently ease the moderate pain, swelling and inflammation of hemorrhoids with home treatments.
- Eat high-fiber foods. Consume more fruits, veggies and entire grains. Doing so softens the stool and increases its bulk, which will help you avoid the straining that can worsen symptoms from existing hemorrhoids. Add fiber to your diet slowly to prevent issues with gas.
- Usage topical treatments. Use an over-the-counter hemorrhoid cream or suppository including hydrocortisone, or use pads including witch hazel or a numbing agent.
- Soak frequently in a warm bath or sitz bath. Soak your anal area in plain warm water for 10 to 15 minutes 2 to 3 times a day. A sitz bath fits over the toilet.
- Take oral pain relievers. You can use acetaminophen (Tylenol, others), aspirin or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) briefly to help alleviate your discomfort.
With these treatments, hemorrhoid symptoms often go away within a week. See your physician in a week if you don’t get relief, or sooner if you have severe pain or bleeding.
Medications
If your inflamed hemorrhoids produce just mild discomfort, your doctor may suggest over-the-counter creams, ointments, suppositories or pads. These products contain active ingredients such as witch hazel, or hydrocortisone and lidocaine, which can temporarily relieve pain and itching.
Don’t use a non-prescription steroid cream for more than a week unless directed by your doctor because it can thin your skin.
You can buy appreciate creams and other medications to treat inflamed hemorrhoids on Amazon.
External hemorrhoid thrombectomy
If a painful embolism (apoplexy) has actually formed within an external hemorrhoid, your medical professional can remove the hemorrhoid, which can offer timely relief. This treatment, done under local anesthesia, is most effective if done within 72 hours of establishing a clot.
Minimally invasive procedures
For persistent bleeding or painful hemorrhoids, your doctor might recommend one of the other minimally invasive procedures readily available. These treatments can be performed in your physician’s office or other outpatient setting and don’t generally require anesthesia.
Rubber band ligation. Your physician places one or two small elastic band around the base of an internal hemorrhoid to cut off its blood circulation. The hemorrhoid withers and falls off within a week.
Inflamed hemorrhoid banding can be uncomfortable and cause bleeding, which may start 2 to four days after the treatment but is hardly ever severe. Sometimes, more-serious complications can take place.
- Injection (sclerotherapy). Your medical professional injects a chemical service into the hemorrhoid tissue to shrink it. While the injection causes little or no pain, it might be less effective than elastic band ligation.
- Coagulation (infrared, laser or bipolar). Coagulation techniques use laser or infrared light or heat. They trigger small, bleeding internal hemorrhoids to harden and shrivel. Coagulation has few side effects and usually triggers little discomfort.
Surgical procedures
Just a little percentage of individuals with hemorrhoids require surgery. However, if other treatments haven’t been successful or you have large hemorrhoids, your physician might advise one of the following:
Hemorrhoid removal (hemorrhoidectomy). Choosing one of various strategies, your surgeon eliminates extreme tissue that triggers bleeding. The surgery can be done with local anesthesia combined with sedation, spine anesthesia or general anesthesia.
Hemorrhoidectomy is the most reliable and complete method to treat extreme or repeating hemorrhoids. Issues can consist of short-lived problem clearing your bladder, which can lead to urinary tract infections. This issue occurs primarily after spine anesthesia.
Most people have some pain after the procedure, which medications can ease. Soaking in a warm bath also might help.
Hemorrhoid stapling. This procedure, called stapled hemorrhoidopexy, obstructs blood flow to hemorrhoidal tissue. It is usually used only for internal hemorrhoids.
Stapling typically involves less pain than hemorrhoidectomy and enables earlier return to routine activities. Compared to hemorrhoidectomy, however, stapling has actually been connected with a greater risk of recurrence and rectal prolapse, in which part of the rectum protrudes from the anus.
Issues can also consist of bleeding, urinary retention and pain, along with, rarely, a deadly blood infection (sepsis). Talk with your physician about the best alternative for you.
When hemorrhoids become inflamed – what to do
Treatment of inflamed hemorrhoids is carried out in three ways:
- Normalization of stool;
- Observance of personal hygiene;
- Medication therapy.
Patients are advised to exclude the following foods from their diet:
- Flour products (including noodles and pasta);
- Rice and semolina porridge;
- Potatoes;
- Coffee and chocolate;
- Potatoes;
- Milk;
- Cigarettes and alcohol (iythealth.com recommends leaving these bad habits for good).
Fresh fruits and vegetables and wholemeal bread should be added to the menu. Patients are advised to drink plenty of fluids and eat cereals from coarse grits for breakfast when hemorrhoids are inflamed. It is necessary to go to the toilet at the same time, to replace toilet paper by washing with cool water without irritants, to refuse insolation, visits to the sauna, sauna.
Medication therapy for inflammation of hemorrhoids
To normalize stool, proctologists prescribe patients who have inflamed hemorrhoids, enzyme preparations, eubiotics, means that affect the motility of the colon, wheat bran, dietary fiber, seaweed, linseed preparations. With the prevalence of constipation normalize the water balance – patients are advised to consume sufficient fluids against the background of the application of drugs. Proctologists prescribe laxatives: lactulose, regulax, phytomucil, mucofalk.
Basic therapy for inflammation of hemorrhoids includes phlebotropic drugs. They have venotonic and angioprotective effect, decrease venous distensibility and venous stasis, decrease capillary permeability and increase their resistance. Under the influence of these drugs the venous outflow in the inflamed area is normalized.
Local treatment of hemorrhoid inflammation is aimed primarily at eliminating the pain syndrome. It is usually caused by spasm of the anal sphincter, which occurs with hemorrhoid inflammation. Proctologists prescribe ointments and rectal suppositories.
If the inflammation of hemorrhoids occurred against the background of thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal nodes, local anticoagulants in the form of suppositories and combined ointments are used. For hemorrhoidal thrombosis and inflammation, heparin and troxevasin ointments are used. If thrombosis of hemorrhoidal nodes is complicated by inflammation with the transition to the subcutaneous tissue and perianal area, these drugs are used in combination with ointments that have anti-inflammatory properties (levosin, levomecol).
If the patient has inflamed hemorrhoids, doctors of the proctology department conduct systemic therapy with phlebotropic drugs. The most effective is diosmin. In 98% of patients treated with diosmin, there is a subsidence of inflammation and the frequency of annual exacerbations is reduced by 2.2 times.
Despite the use of modern effective drugs, conservative treatment, which is carried out when hemorrhoids are inflamed, is only a palliative measure and gives short-term positive effect. Resumption of constipation, errors in diet, increased physical activity leads to another exacerbation. That is why if this type of treatment is inefficient, especially in advanced stages of the disease, doctors at the proctology department perform a combined treatment. It includes conservative and minimally invasive methods or conservative and traditional surgical methods:
- Ligation of hemorrhoidal nodes with latex rings;
- Hemorrhoidal node sclerosing;
- Proximal ligation of hemorrhoidal nodes;
- Hemorrhoidectomy.
Since it is impossible to independently diagnose and assess the severity of inflammation of the hemorrhoidal nodes, and self-treatment, inadequate therapy can lead to quite serious complications.