What is back or intervertebral disc? It is one of the rubbery cushions (discs) in between specific bones (vertebrae) that accumulate to make your spinal column. It is somewhat like a jelly donut with a soft center (nucleus pulposus) within a soft exterior (annulus fibrosus).
What is a Herniated Disc?
Disc herniation occurs when a few of the softer “jelly” presses out through a fracture in the difficult exterior. A herniated disc can irritate close-by nerves and lead to pain, numbness or weakness in an arm or leg. Herniated disc is also described as a slipped disc or a burst disc.
What are the Symptoms of Herniated Disc Disease?
Your symptoms might vary based on the location of your herniated disc. Often you may experience no symptoms. Most herniated discs take place in the lower back (lumbar spinal column) or neck (cervical spinal column).
The common symptoms connected with herniated disc are:
- Back or neck pain.
- Sciatica.
- Weakness, numbness, or pain in arms or legs.
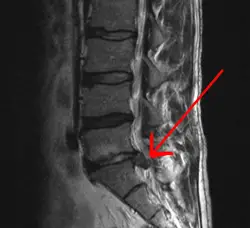
Spinal disc herniation
What are the Risk Factors Connected with Spine Disc Herniation?
The majority of people are unable to pinpoint the specific cause of disc herniation. Risk factors connected with disc herniation include:
- Aging: Aging associated wear & tear can cause disc degeneration. This makes the back disc more to prone to tearing or rupture even with a minor strain or twist.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can cause additional stress on your discs
- Physically requiring tasks/ Lifting heavy objects: Using back muscles instead of your leg muscles to raise objects or turning or twisting when raising heavy objects can lead to disc herniation.
- Injury or distressing events: A fall, a blow to the back or an automobile mishap.
When do I Need to See a Doctor?
You must look for immediate medical attention if you experience getting worse symptoms, such as:
- Inability to carry out activities of everyday living.
- Increasing back or neck pain.
- Increasing weakness or numbness of arms or legs.
- Radiating pain.
- Back or neck pain traveling down your arm or leg.
- Bowel or bladder dysfunction.
How do We Diagnose Herniated Disc Disease?
Dr. Goswami is a knowledgeable interventional pain management doctor with outstanding outcomes. He got interventional pain management fellowship training at Weill Cornell Medical College, New York. After his fellowship training, Dr. Goswami established Multidisciplinary Interventional Pain Clinic at New Mexico Veteran Hospital in Albuquerque, New Mexico. On relocating to NYC, he founded Epic Pain Management in 2010.
He has received many awards from the leading independent healthcare score business. We likewise receive numerous testimonials from Dr. Goswami’s patients complimenting him on his professionalism, empathy and ability.
Case history and physical examination can normally identify any serious conditions that may be triggering the pain.Imaging tests are not called for in many cases. Under specific situations, nevertheless, imaging might be bought to dismiss specific causes of pain, including herniated disc or spine stenosis. Imaging and other types of tests include:
- Computerized tomography (CT) & Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Myelograms.
- Discography.
- Electromyography (EMG), Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS), and Evoked Potential (EP) research studies.
How does Dr. Goswami treat herniated disc disease?
The goal of our treatment is practical rehab. While getting rid of chronic back or neck pain is incredibly hard, our functional rehabilitation program looks for to return patients to levels of activity that they had the ability to carry out prior to experiencing back or neck pain. We have a multimodal technique to treatment, where we use several methods to treat pain.
Our multimodal method includes:
-
Muscle strengthening program
We motivate our patients to start stretching exercises and resume normal daily activities as quickly as possible, while preventing movements that worsen pain. Physical therapy programs to strengthen core muscle groups that support the low back, improve movement and versatility, and promote appropriate positioning and posture are typically used in combinations with other interventions.
-
Medications
Medical routine usually consists of anticonvulsants, antidepressants and counter irritants such as capsaicin.
-
Minimally Invasive Treatment
Nerve block therapies intend to alleviate chronic pain by blocking nerve conduction from specific areas of the body. Nerve block approaches range from injections of anesthetics, botulinum contaminant, or steroids into afflicted soft tissues or joints to more intricate nerve root blocks and spinal cord stimulation. The success of a nerve block method depends upon the capability of a specialist to find and inject exactly the right nerve. Some of the common treatment alternatives include:
-
Epidural Steroid Injection
Epidural space is a prospective area within the spinal canal. It surrounds the outermost covering of the spinal cord (dura mater). It consists of nerve roots, blood vessels & fat. A reasonably percentages of corticosteroids together with a local anesthetic are injected into the epidural area around the spine and spine nerves.
The anti-inflammatory impacts of the corticosteroid is accountable for providing pain relief. Epidural Steroid Injections help patients struggling with disc herniation, disc bulges, degenartive disc disease, sciatica & spinal stenosis. It is thought about to be an important part of nonsurgical management of radicular pain from back disorders.
-
Endoscopic Discectomy
Endoscopic Discectomy is a procedure used to remove damaged disc product in the spine. It is a minimally invasive discipline that unlike the conventional procedure does not involve significant tissue injury. Instead, a small metal tube, the size of a pencil, is placed into the herniated disc area under x-ray assistance.
The tube works as a passage for the surgical tools and a tiny cam (endoscope). Under the guidance of real-time x-ray image (fluoroscopy) and a magnified live video feed, the fragment of the disc pinching the nerve is eliminated. You might take advantage of discectomy if your discussion consists of: Pain, numbness or weakness in arms or legs or imaging studies reveal disc problems such as disc annular tear, disc bulge, or disc herniation.
Spinal Cord Stimulator (SCS) consists of promoting electrodes, implanted in the epidural area, an electrical pulse generator, implanted in the lower abdominal area or gluteal region, conducting wires connecting the electrodes to the generator, and the generator push-button control. SCS has significant analgesic properties and, at the present, is used mostly in the treatment of failed back surgery syndrome, complicated local pain syndrome and refractory pain due to ischemia.
Surgery
Surgery is generally scheduled for few patients with pain from structural physiological problems that have not reacted to medical or interventional therapy.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.