Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease that causes lasting inflammation and ulcer symptoms, or sores in the digestive tract. Ulcerative colitis affects the innermost lining of the large intestinal tract and anus.
What is Ulcerative Colitis?
This inflammatory disease can be incapacitating, and in some cases it can even lead to lethal complications. Ulcerative colitis might lead to a narrowed area of the intestinal tracts, making it harder to pass stool. It may likewise cause swelling in the colon, intense diarrhea, joint pain, and scarring of the bile ducts and pancreas.
Ulcerative colitis usually starts gradually and can become worse over time. The symptoms of this inflammatory disease can be mild to severe, and the majority of people have periods of remission, times when the symptoms disappear, which can last for weeks or years.
While there is no known treatment for ulcerative colitis, there are natural treatments that can considerably reduce symptoms and signs of the disease and lead to long-term remission.
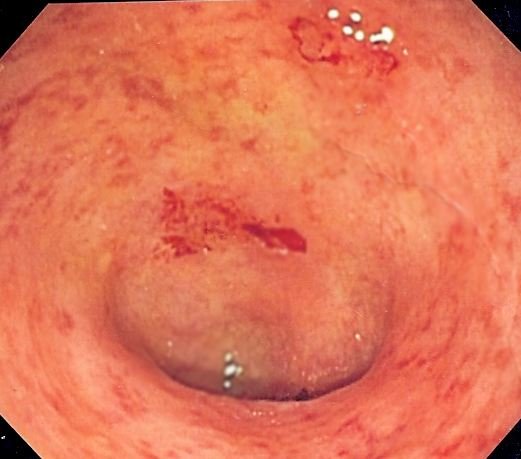
Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease that results in chronic inflammation in the digestive tract, normally in the big intestine (colon) and the rectum.
Symptoms of ulcerative colitis may include:
- Abdominal pain.
- Bloody diarrhea.
- Rectal bleeding.
- Feeling of urgency.
- Failure to have a defecation regardless of the desire to do so.
- Abdominal cramping and pain.
- Weight loss.
Symptoms might also happen outside the gut and include joint pain, eye inflammation, skin rashes and lesions, and mouth ulcers.
Source of Ulcerative Colitis
Diet and stress were always known to be the origin of ulcerative colitis, but recently physicians have concluded that these factors might worsen the inflammatory condition however do not cause it, according to the Mayo Clinic. One possible cause is a body immune system malfunction. When the body immune system aims to battle an attacking virus or germs, an abnormal immune action causes the body immune system to attack the cells in the digestive tract.
Ulcerative colitis typically starts before the age of 30, however there are some cases when individuals did not establish the disease up until after age 60. You are at a higher risk of establishing ulcerative colitis if you have a close relative with the disease, such as a parent or sibling. Another significant risk aspect is a particular medication used to treat scarring cystic acne, called isotretinoin. In studies published in the American Journal of Gastroenterology, a link between the development of ulcerative colitis and isotretinoin was established.
Stress can also cause a flare-up. It’s crucial to avoid stress, particularly chronic stress, by working out, extending, and practicing relaxation techniques and breathing exercises.
Natural Remedies for Ulcerative Colitis
There is no known remedy for ulcerative colitis. Alternative therapies are popular amongst individuals with ulcerative colitis, however, so far scientific support for the claim that any remedy can treat ulcerative colitis is doing not have. It’s essential to keep in mind that natural medicine needs to not be used as a substitute for basic care.
Here are 8 natural remedies to consider:
Probiotics
Probiotics, “friendly” bacteria that reside in the gut, have been found to be reliable in handling ulcerative colitis. They help manage the number of possibly harmful bacteria, reduce inflammation, and enhance the protective mucus lining of the gut.
Probiotics are among the most popular remedies for inflammatory bowel disease because they lack substantial side effects and seem safe for the majority of people.
A University of Alberta study analyzed 34 individuals with mild-to-moderate active ulcerative colitis who were unresponsive to standard treatment.
The scientists gave them a probiotic supplement called VSL # 3, which supplied an overall of 3,600 billion bacteria a day for 6 weeks. At the end of the research study, 18 people (53 percent) showed remission on a sigmoidoscopy and an additional 8 people (24 percent) had a beneficial response.
An Italian research study analyzed the probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii, which was previously found to be beneficial in the maintenance of the other inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s disease. Researchers offered 25 patients with a mild-to-moderate flare-up of ulcerative colitis a supplement containing 250 milligrams of Saccharomyces boulardii 3 times a day for 4 weeks during upkeep treatment with the drug mesalazine (these patients disagreed for steroid therapy). Of the 24 patients who finished the research study, 17 had scientific remission, which was verified by endoscopic test.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Some studies have discovered that omega-3 fatty acids, discovered in fish oil capsules, may reduce inflammation in people with ulcerative colitis.
A vital analysis released in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition looked at regulated trials released from 1966 to 2003. Although the scientists concluded that more proof is needed about the efficacy of omega-3 fatty acids, three studies discovered that omega-3 fatty acids decreased corticosteroid requirements (statistical significance was shown in one of these studies.
Another research study took a look at the influence of fish oil and an elemental diet on the digestive tissues of ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s, and control patients and discovered the most significant anti-inflammatory effect in ulcerative colitis tissues.
Research conducted at the Cleveland Clinic took a look at an oral supplement containing fish oil, soluble fiber, and antioxidants (vitamin E, C, and selenium) on disease activity and medication use in adults with mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis. In the research study, 86 patients with ulcerative colitis consumed 18 ounces of the supplement daily for 6 months.
Patients taking the oral supplement had a considerably higher rate of reducing their dose of prednisone over 6 months. More research on omega-3 fatty acids is needed, particularly at differing dosages, due to the fact that not all research studies have discovered a favorable effect.
Oral Aloe Vera Gel
Aloe vera gel has been discovered in research studies to have an anti-inflammatory effect.
A double-blind, randomized trial analyzed the effectiveness and safety of aloe vera gel for the treatment of mild-to-moderate active ulcerative colitis.
Boswellia
Boswellia is a herb that originates from a tree native to India. The active component is the resin from the tree bark, which has actually been discovered to obstruct chemical reactions associated with inflammation. It is used by people with ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions. Unlike anti-inflammatory medication, boswellia does not seem to cause gut irritation that can occur with numerous conventional painkiller.
A 1997 research study of people with ulcerative colitis found that 82 percent of those who took a boswellia extract 350 milligrams 3 times day-to-day knowledgeable remission. Uncommon side effects of bowellia include diarrhea, queasiness, and skin rash.
Boswellia is offered in pill kind. It needs to state on the label that it is standardized to include 60 percent boswellic acids. It ought to not be considered more than 8 to 12 weeks unless under the guidance of a qualified health practitioner.
Diet
A Japanese research study examined the function of dietary elements on inflammatory bowel disease. Consisted of in the study were 111 individuals with ulcerative colitis who were given food surveys.
The survey found a greater intake of sugary foods was favorably connected with ulcerative colitis risk. Vitamin C was discovered to have a protective impact. A higher consumption was related to a lower risk of ulcerative colitis.
Examples of foods rich in vitamin C are red bell peppers, parsley, strawberries, and spinach.
A research study in the journal Gut kept an eye on ulcerative colitis patients in remission for one year using food questionnaires. Consumption of meat, particularly red and processed meat, protein increased the probability of regression. Researchers hypothesize that the high sulphur or sulphate compounds in many of these foods is the offender, considering that high sulfur or sulphate intakes were likewise connected with relapse.
Carbs might be an offender for some people. The Specific Carbohydrate Diet was promoted by Elaine Gottschall after she used it to help her child recover from ulcerative colitis.
Gottschall later wrote a book called Breaking the Vicious Cycle. The premise of the book is that carbohydrates, being kinds of sugar, could promote and sustain the growth of bacteria and yeast in the intestinal tracts, triggering an imbalance and eventually bacterial overgrowth or yeast overgrowth.
The bacteria and yeast produce toxic substances and acids which hurt the intestinal tract lining and they also impair the function of digestive enzymes, which hinders the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates.
Folic Acid
People with chronic ulcerative colitis are at greater risk of colon cancer. A University of Toronto research study found that dietary folate supplementation at four times the standard dietary requirement significantly suppressed ulcerative colitis-associated colon cancer. The incidence of high grade lesions in the folate-supplemented group was 46 percent lower than that in the control group.
Bromelain
Bromelain, a mixture of protein-digesting enzymes originated from pineapple stem, is believed to reduce inflammation. A Duke University animal research study discovered that everyday treatment with oral bromelain reduced the incidence and seriousness of colitis.
Foods that Make Ulcerative Colitis Worse
The foods that make ulcerative colitis even worse typically depend upon the person and the location of inflammation. For some individuals, fiber is irritating during flare-ups due to the fact that high-fiber foods are harder to absorb. Eliminating fibrous foods like nuts, seeds, entire grains, and raw vegetables and fruits from the diet is often called a low-residue diet. Although this can help people with ulcerative colitis to reduce pain, cramps and other symptoms, it does not get rid of inflammation.
If raw vegetables and fruits lead to discomfort, it may help to steam, bake or stew them. This makes foods in the cabbage family, such as nutrient-dense broccoli and cauliflower, simpler to absorb. Some other troublesome products include spicy and fatty foods and caffeinated, carbonated beverages.
People with ulcerative colitis might have difficulty with these foods and drinks:
- caffeine
- carbonated drinks
- dairy products (for individuals who are lactose intolerant or sensitive)
- raw vegetables and fruits
- seeds
- dried beans, peas and beans
- dried fruits

- foods that have sulfur or sulfate
- high-fiber foods
- meat
- nuts and crispy nut butters
- popcorn
- products that have sorbitol (like sugar-free gum and sweets)
- refined sugar
- spicy foods.
Herbal Remedies
A few well-known natural home remedy for the management of ulcerative colitis include:
- Psyllium seed/husk enhance gut motility, alleviate the symptoms of constipation, and enhance the removal of waste.
- Boswellia is a naturally taking place herb acquired from the resin part of tree bark. The main mode of action of boswellia in the management of ulcerative colitis is inhibition of specific chain reactions that produce inflammatory mediators.
- Bromelain is commercially readily available in supplemental solutions and consists of proteolytic enzymes that minimize the symptoms and reduce the frequency of flares.
- Probiotics present healthy gut bacteria to bring back and preserve a natural microbial flora in the gut. This may reduce damaging inflammatory reactions and keep remission.
- Turmeric, the spice used in curry, might help patients with ulcerative colitis. Particularly, the curcumin discovered in turmeric appears to improve the efficiency of standard medical therapy.
- Gingko biloba has actually been effective in treating speculative colitis in rodents, but this has actually not been displayed in humans.
Using Natural Remedies
Supplements and other forms of alternative medicine have not been checked for safety in pregnant women, nursing mothers, children, and those with medical conditions or who are taking medications. You can get suggestions on using supplements here however must constantly talk to your medical care company prior to using supplements or natural medicine or making a change to your routine. Delaying or avoiding basic care can have serious repercussions.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.







