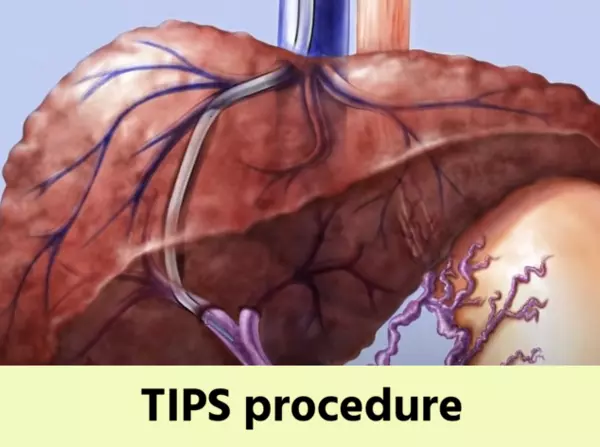
The Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) is a well-established percutaneous modality used to decrease portal hypertension. This procedure relieves high blood pressure in the portal vein, which often occurs in the setting of liver disease. TIPS allows blood to bypass the liver and flow directly from the portal vein to the hepatic vein, reducing the risk of complications such as variceal bleeding and ascites.
However, TIPS does come with potential risks and limitations that need to be carefully considered.
We will explore the ins and outs of TIPS, its benefits, risks, and alternatives, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this important procedure.
Overview
TIPS is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat complications of portal hypertension, a condition characterized by increased blood pressure in the portal vein, which carries blood from the digestive organs to the liver.
TIPS involves the creation of a shunt, or bypass, between the portal vein and one of the hepatic veins, allowing blood to flow directly through the liver. This helps to relieve pressure in the portal vein and prevent complications such as variceal bleeding and ascites.
TIPS is typically performed by interventional radiologists using fluoroscopy and ultrasound guidance. The procedure involves making a small incision in the neck to access the jugular vein, through which a catheter is threaded to the liver. A stent is then placed to create the shunt.
TIPS can be an effective treatment option for patients with severe portal hypertension who are not responsive to medication or other interventions. It can improve symptoms and quality of life, reduce the risk of complications, and extend survival.
However, TIPS is not without risks and potential complications, including infection, bleeding, and hepatic encephalopathy. Careful patient selection, vigilant monitoring, and prompt management of complications are essential for ensuring the success and safety of the procedure.
Recovery after TIPS can vary depending on individual factors and the presence of underlying liver disease. Most patients are able to leave the hospital within a few days and resume normal activities within a week.
Long-term follow-up is necessary to monitor the effectiveness of the shunt and manage any complications that may arise.
Explanation of its purpose and benefits
The purpose of TIPS is to create a shunt or connection between the portal vein and hepatic vein, bypassing the liver and reducing pressure in the portal system. This helps to alleviate symptoms and complications caused by portal hypertension, such as variceal bleeding and ascites.
The benefits of TIPS include:
- Variceal bleeding prevention: By reducing portal pressure, TIPS can help prevent life-threatening bleeding from varices, dilated veins in the esophagus or stomach.
- Ascites management: TIPS can also improve ascites by reducing fluid buildup in the abdomen. It helps to relieve symptoms like abdominal distension and difficulty breathing.
- Hepatic hydrothorax treatment: TIPS has been shown to be effective in managing hepatic hydrothorax, a buildup of fluid in the pleural cavity, reducing the need for repeated thoracentesis and improving symptoms.
- Improved quality of life: TIPS can significantly improve the quality of life for patients with advanced liver disease by reducing complications, hospitalizations, and the need for invasive procedures.
Step-by-step guide to the TIPS procedure
- Pre-operative Preparation:
- The patient is given instructions on fasting and medication management.
- An intravenous line is established for administering medication.
- Anesthesia:
- The patient is placed under local anesthesia to numb the area of the neck where the catheter will be inserted.
- Catheter Insertion:
- A small incision is made in the neck.
- A catheter is inserted into the jugular vein and guided towards the liver using fluoroscopy.
- Accessing the Liver:
- The catheter is advanced into the liver and positioned within a hepatic vein.
- Portal Vein Access:
- Using a transjugular needle, the hepatic vein is punctured to reach the portal vein.
- A wire is threaded through the needle into the portal vein.
- Dilating the Tract:
- Over the wire, a series of dilators are passed through the tract to widen it.
- Stent Placement:
- A metal stent is inserted over the wire and placed between the portal vein and hepatic vein to create a shunt.
- The stent expands to keep the shunt open.
- Confirmation and Testing:
- Blood flow within the shunt is confirmed using contrast dye and X-ray imaging.
- Pressure measurements are taken to assess the effectiveness of the shunt.
- Catheter Removal:
- Once the procedure is complete, the catheter is removed.
- Pressure is applied to the access site to prevent bleeding.
- Recovery:
- The patient is monitored for a few hours to ensure stability.
- Pain medication may be provided.
- A follow-up appointment is scheduled to monitor the shunt’s function.
It’s important to note that the TIPS procedure is performed in a hospital setting by a specialized interventional radiologist or hepatologist. The exact steps may vary depending on the specific case and the expertise of the medical team involved.
Role of imaging techniques during the procedure
During the Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedure, imaging techniques play a crucial role in guiding the placement of the shunt. The most commonly used imaging modality is fluoroscopy, which provides real-time X-ray images that allow the interventional radiologist to visualize the liver, hepatic veins, portal vein, and other relevant structures.
Additionally, ultrasound imaging may be used to assist with the initial identification of the hepatic vein during the procedure. This helps ensure accurate placement of the shunt. Doppler ultrasound may also be used to assess blood flow before and after the shunt placement, providing valuable information about the patency and functionality of the shunt.
The use of advanced imaging techniques, such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be employed before the procedure to assess the anatomy of the liver and the portal venous system. This helps the interventional radiologist determine the feasibility and appropriateness of TIPS for each individual patient.
By utilizing these imaging techniques, the interventional radiologist can navigate the complex blood vessels and perform the TIPS procedure with precision, minimizing the risk of complications and optimizing the outcomes for patients.
Here’s a quick summary of the role of imaging techniques during the TIPS procedure:
- Fluoroscopy: Real-time X-ray imaging for visualizing liver, hepatic veins, and the portal vein during the procedure.
- Ultrasound: Helps identify the hepatic vein, assess blood flow, and evaluate shunt functionality.
- CT or MRI: Provides pre-procedural assessment of liver anatomy and portal venous system.
Using these imaging techniques, the interventional radiologist can confidently perform the TIPS procedure while ensuring patient safety and efficacy.
Conditions that may require TIPS
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is a procedure that is commonly used to treat various conditions related to liver disease. Some of the conditions that may require TIPS include:
- Portal hypertension: TIPS is often performed in patients with portal hypertension, which is an increase in blood pressure within the portal vein system that drains blood from the intestines, pancreas, and spleen into the liver.
- Ascites: TIPS can be used to treat ascites, which is the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen.
- Variceal bleeding: TIPS may be performed in patients who are experiencing variceal bleeding, which is bleeding that occurs in enlarged veins in the esophagus or stomach.
These conditions can be related to various liver diseases, such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, or liver cancer. TIPS is often considered when other treatments have not been successful or are not feasible. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if TIPS is the appropriate treatment option for your specific condition.
Factors that may affect eligibility for TIPS
Factors that may affect eligibility for TIPS (Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt) can vary depending on the specific patient case, but the following are some common considerations:
- Severity of liver disease: TIPS is typically considered for patients with severe liver disease, such as cirrhosis, who have complications like portal hypertension. The severity of the liver disease and the extent of complications will influence the decision for TIPS.
- Response to medical therapy: Before considering TIPS, patients are often prescribed medications and other treatments to manage their liver disease and associated complications. The effectiveness of these treatments and the patient’s response to them will be considered when determining TIPS eligibility.
- Portal vein thrombosis: If there is complete blockage of the portal vein, TIPS may not be possible or may carry higher risks. The presence of portal vein thrombosis will be evaluated during imaging studies to assess eligibility for TIPS.
- Liver function: The overall function of the liver is an important factor in determining TIPS eligibility. This is usually assessed using blood tests that measure liver enzymes, bilirubin levels, and other markers of liver function.
- General health and comorbidities: The patient’s overall health and presence of other medical conditions will be considered. TIPS is a procedure that involves some level of risk, so the patient’s ability to tolerate the procedure and potential complications will be taken into account.
- Cardiac function: TIPS involves manipulating blood flow and pressure within the liver, which can affect the cardiovascular system. Patients with significant cardiac issues may not be suitable candidates for TIPS.
- Ability to follow post-procedure care: TIPS requires ongoing management and potentially lifestyle modifications after the procedure. Patients must be able to follow the necessary care instructions to ensure the success and long-term efficacy of TIPS.
These factors are general guidelines and that each patient’s case is unique. A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional specializing in liver disease and interventional radiology is necessary to determine TIPS eligibility.
Potential risks and complications associated with TIPS
Although Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is generally considered a safe procedure, there are potential risks and complications that patients should be aware of. These include:
- Procedure-related risks: TIPS is performed under local anesthesia and carries a small risk of bleeding, infection, or damage to the blood vessels or surrounding organs involved in the procedure.
- Portal vein thrombosis: TIPS may increase the risk of blood clots forming in the portal vein, which can potentially lead to portal vein thrombosis. This complication may require additional treatment.
- Heart failure: TIPS can cause an increase in blood flow to the liver, which may put extra strain on the heart. Patients with pre-existing heart conditions are at a higher risk of developing heart failure after TIPS.
- Encephalopathy: TIPS can lead to a condition called hepatic encephalopathy, where toxins build up in the brain due to decreased liver function. Symptoms may include confusion, changes in behavior, and difficulty with coordination.
- Hepatic artery injury: There is a small risk of injury to the hepatic artery, which may cause bleeding or reduced blood supply to the liver.
- Recurrence of symptoms: Although TIPS is effective in relieving portal hypertension and related symptoms, there is a possibility of recurrent symptoms over time, requiring additional intervention or further TIPS procedures.
Patients considering TIPS should discuss these potential risks and complications with their healthcare provider to ensure that they have a clear understanding of the procedure and can make an informed decision. It is important to note that the overall risks and benefits of TIPS will vary depending on each individual’s specific medical condition and the presence of any additional risk factors.
Ways to minimize and manage these risks
To minimize and manage the risks associated with Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedures, healthcare professionals follow specific protocols and precautions:
- Thorough patient evaluation: Proper patient selection and assessment of factors such as liver function, clotting disorders, and other medical conditions are crucial in minimizing risks.
- Experienced medical team: TIPS procedures should be performed by experienced interventional radiologists or hepatologists who have expertise in the technique to ensure safety and success.
- Pre-procedure preparation: Prior to the TIPS procedure, patients may undergo blood testing, imaging studies, and consultations to determine the appropriateness of the procedure and identify any potential complications in advance.
- Anticoagulation management: Careful management of anticoagulant medications before and after TIPS can minimize the risk of bleeding complications. Close monitoring of coagulation parameters is essential.
- Infection control: Strict adherence to sterile techniques during the procedure reduces the risk of infection. Antibiotics may be administered before and after TIPS to prevent or manage infection.
- Radiological guidance: The use of advanced imaging techniques such as ultrasound, fluoroscopy, or angiography during the TIPS procedure allows precise positioning of the shunt, minimizing the risk of complications.
- Post-procedure monitoring: Close monitoring of patients after the TIPS procedure for any signs of complications such as bleeding, infection, or hepatic encephalopathy is crucial. Regular follow-up visits and imaging studies help detect and manage any complications promptly.
- Medication management: Appropriate medication management, including diuretics and lactulose, can help prevent or manage complications such as hepatic encephalopathy.
- Patient education: Comprehensive patient education about the procedure, potential risks, and signs of complications empowers patients to seek medical attention promptly and actively participate in their recovery process.
Despite these measures, risks and complications can still occur. Close collaboration between patients, healthcare professionals, and multidisciplinary teams is essential to effectively manage and minimize these risks.
Expected recovery process after TIPS
After undergoing a TIPS procedure, the expected recovery process varies depending on the individual and the specific condition being treated. Generally, patients can expect to stay in the hospital for a few days following the procedure for close monitoring. During this time, healthcare professionals will assess the patient’s vital signs, liver function, and any potential complications. Pain medication will be provided as needed to manage discomfort.
Once discharged, patients should expect to take it easy for a period of time, gradually resuming normal activities under the guidance of their healthcare team. It’s important to note that some patients may experience temporary side effects such as fatigue, abdominal discomfort, or changes in appetite. These symptoms typically improve over time as the body adjusts to the shunt.
Follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor the shunt’s effectiveness and overall liver function. Patients may need to undergo additional imaging tests, such as ultrasounds or CT scans, to assess the shunt’s patency and detect any potential complications.
During the recovery period, it’s essential that patients adhere to any recommended lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes or medication regimens, to ensure the long-term success of the TIPS procedure. Close communication with the healthcare team is crucial to address any concerns or questions that may arise during the recovery process.
It’s important to note that every patient’s recovery experience may vary, and individual circumstances should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Data on the success rate and long-term efficacy of TIPS
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt has been widely studied and has shown significant success in treating various liver-related conditions.
According to research, the success rate of TIPS in controlling bleeding from esophageal varices is around 90%. The procedure has also been found to effectively reduce portal hypertension and improve liver function in patients with cirrhosis.
Long-term studies have shown that TIPS can provide significant relief from symptoms, improve quality of life, and prolong survival in patients with certain liver diseases. However, it is important to note that the success and long-term efficacy of TIPS can vary depending on individual patient factors and the underlying condition being treated.
Close monitoring and follow-up care are crucial to ensuring the continued effectiveness of the procedure.
Comparison to alternative treatment options
When considering treatment options for conditions that may require a TIPS, it’s important to understand the alternatives available. Two common alternatives to TIPS are medication therapy and surgical procedures.
Medication Therapy: Medications can be used to manage symptoms and slow down the progression of certain liver diseases. However, they may not be effective for all patients, and long-term medication use can come with side effects and limitations.
Surgical Procedures: Another alternative to TIPS is surgical intervention, such as a surgical shunt or liver transplant. Surgical procedures are generally more invasive and require a longer recovery time. They may also involve higher risks and costs compared to TIPS.
Here’s a summarized comparison of TIPS, medication therapy, and surgical procedures for treating liver conditions:
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| TIPS | Minimally invasive procedure that creates a shunt between the portal vein and hepatic vein to relieve high blood pressure in the liver. Offers immediate relief of symptoms, reduced risk of variceal bleeding, and improved liver function. Typically performed under local anesthesia and has a relatively short recovery time. |
| Medication Therapy | Involves the use of medications to manage symptoms and slow the progression of liver diseases. Can be effective in certain cases, but may not provide long-term relief or address the underlying causes. Medication therapy can have side effects and limitations, and may require long-term use. |
| Surgical Procedures | Surgical interventions like surgical shunts or liver transplant may be required in more severe cases or when other treatment options are not viable. Surgical procedures are more invasive, carry higher risks, and require longer recovery times compared to TIPS. They may also involve higher costs and longer hospital stays. Surgical procedures are typically performed under general anesthesia. |
Recommendations for lifestyle modifications after TIPS
After undergoing a Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedure, it is important to make certain lifestyle modifications to ensure a successful recovery and maintain overall health. Here are some recommendations to consider:
- Dietary Changes:
- Follow a low-sodium diet to reduce fluid retention and prevent complications.
- Limit alcohol intake to alleviate additional stress on the liver.
- Incorporate a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Fluid Intake:
- Monitor and regulate fluid intake to prevent fluid overload and minimize the risk of complications.
- Consult with a medical professional to determine the appropriate fluid intake for your specific condition.
- Physical Activity:
- Engage in regular physical activity as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Aim for low-impact exercises such as walking or swimming to promote cardiovascular health.
- Medication Management:
- Take all prescribed medications as directed by your healthcare team.
- Discuss any changes in your medication regimen with your doctor before making adjustments.
- Follow-up Care:
- Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor the effectiveness of the procedure and address any concerns.
- Collaborate with your healthcare team to manage any ongoing medical conditions.
It is important to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations and guidelines tailored to your specific needs and medical history. They will be able to provide you with detailed instructions and guidance to optimize your recovery after a TIPS procedure.
Cost considerations for TIPS
When considering the cost of Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedure, it is important to factor in several components. These may include:
- Hospital Expenses: TIPS is an invasive procedure that requires specialized equipment, a skilled medical team, and an operating room. The cost of these facilities and services can vary depending on the hospital and location.
- Surgeon’s Fees: Surgeons who perform TIPS are highly specialized and may charge different fees based on their level of experience and reputation.
- Anesthesia Costs: Since TIPS is performed under anesthesia, there will be additional costs for anesthesia services.
- Imaging and Laboratory Tests: Prior to undergoing TIPS, patients may need to undergo various imaging and laboratory tests to assess their liver function and overall health. These tests can add to the overall cost.
- Follow-up Care: After the TIPS procedure, patients will require regular follow-up appointments and monitoring to ensure the shunt is functioning properly. These ongoing medical visits will also contribute to the overall cost.
| Clinic Name | Location | TIPS Cost |
|---|---|---|
| ABC Medical Center | New York | $25,000 – $30,000 |
| XYZ Hospital | California | $35,000 – $40,000 |
| DEF Clinic | Texas | $28,000 – $34,000 |
| GHI Healthcare | Florida | $30,000 – $36,000 |
| JKL Medical Group | Illinois | $32,000 – $38,000 |
Current research and potential future advancements in TIPS
Current research in Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is focused on improving the procedure’s efficacy, safety, and long-term outcomes. Some potential future advancements in TIPS include:
- Stent Technology: Researchers are exploring the use of innovative stent designs and materials to enhance shunt patency and reduce complications such as stent occlusion or migration.
- Image-Guided Techniques: Advancements in imaging technology, such as three-dimensional angiography and fusion imaging, can provide more precise guidance during the TIPS procedure, improving accuracy and reducing procedural risks.
- Drug-Eluting Stents: The development of drug-eluting stents for TIPS is being investigated to prevent restenosis and improve the long-term efficacy of the shunt.
- Biomarkers and Patient Selection: Researchers are exploring the use of biomarkers and advanced imaging techniques to better predict which patients would benefit most from TIPS and to identify those at higher risk of complications.
- Combined Therapies: Studies are being conducted to evaluate the potential benefits of combining TIPS with other treatment modalities, such as targeted drug therapy or radiation therapy, to improve patient outcomes and reduce the need for repeat interventions.
It is important to note that these advancements are still in the research and development stage and may not be widely available or standardized for clinical use. Patients considering TIPS should consult with their healthcare professionals to understand the most current treatment options and potential advancements relevant to their specific condition
Final thoughts and considerations for patients and healthcare professionals
In conclusion, Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is a highly effective procedure for managing chronic liver disease and its complications. It offers numerous benefits, including reduced portal hypertension, improved symptoms, and decreased risk of variceal bleeding. However, it is crucial for patients and healthcare professionals to consider the following:
- Risks and complications: While TIPS is generally safe, there are potential risks such as infection, bleeding, and hepatic encephalopathy. Patients must be aware of these risks and closely monitored after the procedure.
- Eligibility criteria: Not all patients with liver disease are suitable candidates for TIPS. Factors such as liver function, severity of portal hypertension, and presence of other complications need to be evaluated before proceeding with the procedure.
- Long-term efficacy: TIPS has shown good long-term success rates in managing variceal bleeding and ascites. However, follow-up care and regular monitoring are essential to ensure continued efficacy and detect any potential complications.
- Lifestyle modifications: Patients who undergo TIPS may need to make certain lifestyle modifications, such as dietary restrictions and medication management, to support liver health and minimize the risk of complications.
- Cost considerations: TIPS is a complex and specialized procedure that can be costly. Patients should factor in the financial implications and discuss with their healthcare provider regarding payment options.
- Advancements in TIPS: Ongoing research and advancements in imaging techniques, procedural approaches, and device technology continue to improve the safety and efficacy of TIPS. Patients and healthcare professionals should stay updated on these developments.
The decision to undergo TIPS should be made after thorough consultation with a healthcare professional who can assess the individual’s specific condition and risk factors. Open communication, informed decision-making, and comprehensive post-procedure care are critical for achieving optimal outcomes with TIPS.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.