Each of us encounters bacteria called “staphylococcus aureus” many times in our lives. Moreover, a small number of them may be present in the microflora of a healthy person. Most often the microbe is found on the skin and in the upper respiratory tract. How dangerous is the presence of Staphylococcus aureus in the throat and how to treat the infection if it is already present, iythealth.com will tell you.
Staphylococcus aureus in the throat
Among all types of pathogenic staphylococci, it is the golden staphylococcus that can pose the greatest danger. It is a fairly aggressive bacterium that releases dangerous toxins and enzymes that can destroy tissue. Diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus in the throat are very difficult to treat – the microbe quickly adapts to new conditions and is resistant to many drugs, including penicillin antibiotics of past generations.
According to statistics, one in five people on the planet is a carrier of the bacterium. This is due to the high survival rate of the bacteria in the external environment and to different ways of transmission. Most often staphylococcus gets into the throat by contact – through contaminated objects, dirty hands, unwashed fruits and vegetables. Staphylococcus aureus is especially often transmitted in children, since young children have a habit of pulling various objects into their mouths.
Another way of infection is through airborne droplets. The bacterium spreads easily through the air from a person with an advanced staph infection – through coughing, sneezing, and so on.
Staphylococcus aureus can also be transmitted from mother to child through breast milk. In this case, there is a very high probability of the bacteria settling not only in the throat, but also in the intestines.
Staph infections can turn deadly if the bacteria invade deeper into your body, entering your bloodstream, joints, bones, lungs or heart.
Mayo Clinic
Causes
Infection very often occurs in a hospital setting
Staphylococcus aureus tops the list of pathogens that enter patients in hospital settings.
The range of diseases caused by the bacterium is astounding in its diversity:
- Cutaneous infections – carbuncles, furuncles, phlegmons, folliculitis, bullous impetigo.
- Respiratory tract infections – pneumonia, sore throat.
- Central nervous system infections – meningitis, cerebral abscess, cerebral superficial vein thrombophlebitis.
- Infections of the urinary tract – cystitis, urethritis.
- Infections of bones, joints, musculoskeletal apparatus – osteomyelitis, purulent arthritis, purulent myositis.
Causes of staphylococcal infections include the following factors:
- The presence of chronic diseases;
- Weakened immunity;
- taking a large number of medications;
- Avitaminosis;
- frequent stress;
- Infection from a carrier;
- living conditions that do not meet the standards of sanitation and epidemiology.
Infection with Staphylococcus aureus is particularly dangerous for both children and adults. The microorganisms are highly resistant to most medications and unfavorable external factors.
A feature of this species is its ability to produce endotoxins that cause general intoxication of the body, with late medical intervention – sepsis and infectious-toxic shock.
Immunity to infectious pathogens is not developed, so there is no guarantee that once you catch a disease and get cured, you can not get sick again.
The mechanism of penetration of Staphylococcus aureus into the human body consists of several stages:
- Infestation. From the external environment, the cocci reach the mucous and skin membranes. With the help of a special acid, they attach themselves to the epithelium and begin to produce toxins.
- Penetration through the epithelium and attachment to extracellular elements. The bacteria are unable to penetrate through intact skin and mucous membranes. They penetrate in cases where a person’s natural protective barriers are damaged and the glandular ducts are obstructed. Staphylococci attach to molecules of fibrinogen, laminin, elastin, collagen, and other tissues.
- Tissue Destruction. In the course of its life, Staphylococcus aureus produces a number of enzymes that create a favorable environment for it and toxins that destroy human cell membranes.
- Destruction of immune barriers. Once Staphylococcus aureus enters the body, phagocytes, which are active defenders of the immune system, attack the pests. The bacteria are able to resist their attack and destroy the phagocytic cells themselves. They can also penetrate and live inside phagocytes.
Symptoms of staphylococcus in the throat
The ubiquity of different types of staphylococcus does not yet cause epidemics of various diseases. This is due to the fact that our immune system successfully controls the reproduction and activity of the bacteria, does not allow them to become a threat to human health. Therefore, a detected Staphylococcus aureus in the throat during a bacterial culture in the laboratory does not mean the presence of the infection itself. Treatment should be prescribed only if the patient has pronounced symptoms of the pathological process. It should be said that the activation of Staphylococcus aureus is always clearly visible – the bacterium triggers putrefactive processes, and they are accompanied by various deteriorations.
The disease is characterized by the following signs:
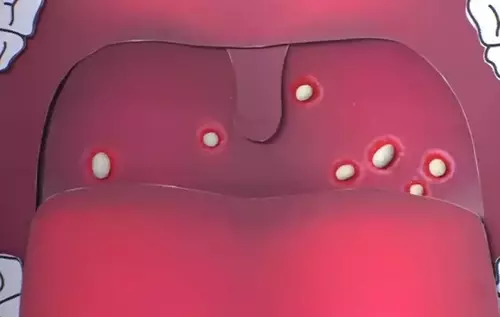
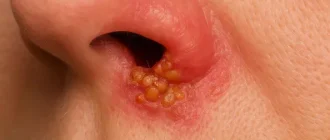
- Inflammation of the tonsils or oropharynx.
- Lumpy surface of the mucosa with the appearance of purulent foci – “white plaque”.
- Perspiration in the throat, hoarse voice.
- Severe sore throat that makes it difficult to swallow.
- Increased temperature, sometimes up to 104°F.
- General intoxication of the body: weakness, drowsiness, loss of appetite, headaches.
Staphylococcal infection differs from the usual acute respiratory infections in that it is not accompanied by a runny nose and is localized on the tonsils. However, given that the bacteria are activated by a lowered immunity, staphylococcus aureus in the throat can appear as a complication of a viral disease. Therefore, if you notice the above symptoms against the background of a cold, it is likely that a bacterial infection has joined the acute respiratory infections.
Anyone can develop a staph infection, although certain groups of people are at greater risk, including people with chronic conditions such as diabetes, cancer, vascular disease, eczema, lung disease, and people who inject drugs.
www.cdc.gov
Staphylococcus aureus in children: pharyngitis, tonsillitis
Since the microbe causes infection only in the case of weakened immunity, staphylococcus in children is a fairly frequent phenomenon. The fact is that the child’s immune system is still being formed, and in the first years, as a rule, the baby is often ill with viral diseases that weaken the body.
Most often children develop pharyngitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis. Bacterial infection is accompanied by the separation of white and yellow sputum and noticeable pustules. Treatment of a child with such diagnoses requires mandatory monitoring by the pediatrician, since staphylococcus aureus can seriously harm children’s health and even lead to life-threatening conditions. With improper or insufficient therapy, staphylococcus aureus in the throat can spread further – to the lungs, heart, enter the bloodstream. The bacterium can infect any organ and tissue.
As a result, staphylococcus in children, causing tonsillitis or pharyngitis, threatens the following complications:
- Pneumonia (lung damage).
- Endocarditis (damage to the heart).
- Meningitis (swelling of the covering of the brain).
- Osteomyelitis (bone damage).
- Sepsis (blood poisoning that leads to a generalized infection). If a child is often ill with bacterial tonsillitis, it is necessary to strengthen its immunity – provide a varied vitamin-rich diet, physical activity, alternate activities and rest, try to walk outdoors as often as possible. It is also necessary to pay attention to and eliminate possible centers of spread of staphylococcus aureus – adenoids, inflamed maxillary sinuses, dental caries.
Treatment of staphylococcal infections
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most resistant bacteria, so the infection caused by it is extremely difficult to treat. Self-treatment or delaying a visit to the doctor is unacceptable. If proper treatment is not begun in time, it can lead to the spread of the infection – Staphylococcus aureus from the throat to the lungs, brain membranes, enters the blood.
The basis of therapy is penicillin antibiotics. However, it should be borne in mind that this particular bacterium is best known for its resistance to medication, and drugs such as Ampicillin now rarely help. Only a doctor can choose the right drug, and ideally for this purpose, antibiotic sensitivity tests should be performed. This is especially relevant for staphylococcal infections in children – such a diagnosis will help to immediately stop at a suitable drug.
The purulent foci themselves must be opened and treated with antibacterial drugs. These procedures are also carried out exclusively by the doctor. Later, the throat is often treated with chlorophyllipt, to which the staphylococcus remains sensitive.
Therapy is supplemented by measures aimed at increasing immunity. In some cases, specific medications and vitamins may be prescribed for this purpose. But more often we are talking about proper nutrition, giving up bad habits, drinking plenty of fluids (to relieve intoxication).

A healthy lifestyle and good hygiene are the best prevention of the development of a staphylococcal infection in the throat, as well as the necessary basis for its treatment.
In order to prescribe effective therapeutic procedures, the patient must first be accurately diagnosed.
To determine the presence of Staphylococcus aureus colonies in the body, the composition of purulent secretions from affected organs and tissues or biological fluids is analyzed.
Biological material from a purulent abscess is stained using the Gram stain method. As a result of research, a large number of cocci and neutrophils (leukocytes) are always detected.
Colonies, samples of which are positive for the presence of coagulase, catalase, and thermonuclease enzymes, with high probability can be attributed to Staphylococcus aureus.
When diagnosing staphylococcal intoxications, the effectiveness of laboratory tests is reduced to zero, they are more of an auxiliary function. Clinical data play an important role in this case.
Conservative treatment of infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus is used only in exceptional cases. Most therapeutic techniques are reduced to the following steps:
- drainage of purulent masses;
- removal of foreign bodies;
- antimicrobial treatment;
- removal of necrotic tissues.
The choice of antibiotics is determined by the type of strain and the degree of its resistance to certain drugs. In practice, the following are used:
- benzylpenicillin;
- cephalosporins (preferably first generation);
- nafcillin;
- oxacillin;
- vancomycin;
- cephalexin.
In mild infections, oral medications are prescribed; in severe cases, antibiotics are administered intravenously.
The duration of treatment depends on how the patient feels, how effective the medications used are, and the severity of the infection. Severe illnesses require a four-week course of medication.
The introduction of measures to reduce the risk of infection with Staphylococcus aureus in hospital rooms plays a special role.
Staphylococcus aureus is a dangerous type of bacteria that causes many infections when the patient’s immune system is weakened. When the first general symptoms (lethargy, nausea, lack of appetite) are detected, it is necessary to see a doctor immediately. The main treatment program for staphylococcal infections is to take antibiotics.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.