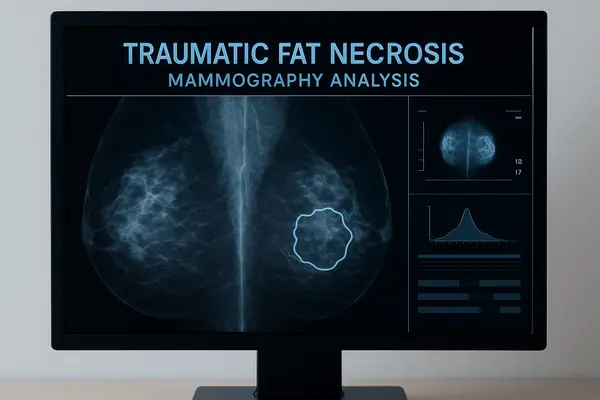
Traumatic fat necrosis occurs when fatty tissue is damaged by physical trauma, surgery, or injections, leading to the breakdown of fat cells and the formation of firm nodules under the skin. The body treats these areas as injured tissue, triggering inflammation and eventually encapsulating the damaged fat in scar-like tissue. In simple terms, it’s like a small internal bruise that hardens instead of healing smoothly. This process is often seen in soft tissues of the breast, thigh, or buttocks, and while it may look alarming, it’s typically benign. In some cases, early tissue injury may be described as subnecrosis—a preliminary stage before full necrosis develops.
From Bump to Clarity: The Patient Journey
This infographic outlines the usual timeline from the first moment a lump appears to complete healing, showing what happens during each stage of traumatic fat necrosis.
Stage 1
Days 0–7
The patient discovers a small firm lump soon after trauma or minor surgery. The area may feel sore or slightly swollen, often mistaken for a simple bruise.
Stage 2
Weeks 2–4
Medical consultation takes place. An ultrasound or MRI is usually ordered to rule out infection or malignancy. The patient receives reassurance once benign fat necrosis is suspected.
Stage 3
Weeks 4–8
Imaging confirms the diagnosis of fat necrosis. Discomfort may persist but generally decreases. The patient begins to see gradual improvement as inflammation subsides.
Stage 4
Months 3–12
Observation continues. The lump gradually softens, and the tissue returns to normal. Follow-up imaging ensures there are no new or suspicious changes.
Stage 5
Beyond 12 Months
Most patients achieve complete recovery. In some cases, small calcifications may remain visible on imaging, but these are harmless and don’t require treatment.
Source: iythealth.com
Case Example: A 42-year-old woman from Dallas, Texas, developed firm nodules under the skin of her lower abdomen following a minor car accident. Initially mistaken for lipomas, imaging confirmed post-traumatic fat necrosis. Over six months, the nodules softened without medical intervention.
Breasts
Traumatic fat necrosis of the breast is one of the most common locations for this condition, often following breast surgery, biopsy, or blunt trauma. It can mimic the appearance of breast cancer on both clinical examination and imaging, causing anxiety for patients. Typically, the affected area feels firm or lumpy, and skin dimpling or redness may appear. In mammography or MRI, the necrotic fat shows characteristic radiologic patterns that help distinguish it from malignant lesions ⧉. According to the American Cancer Society, traumatic fat necrosis accounts for around 0.6% of all benign breast lesions in women in the U.S. ⧉.
Costs & Practicalities of Diagnostic Imaging
This infographic presents the average out-of-pocket cost for different diagnostic tests used to evaluate traumatic fat necrosis, helping patients estimate expenses in both U.S. dollars and euros.
Ultrasound
$150–$350
€140–€320
The most affordable and widely available test. Offers real-time imaging to confirm benign fat necrosis and rule out infection.
Mammography
$100–$250
€90–€230
Commonly used for breast evaluation. Detects calcifications or oil cysts typical for fat necrosis and distinguishes them from malignancy.
MRI (with contrast)
$400–$800
€370–€750
Provides the highest diagnostic detail, ideal when ultrasound results are inconclusive or when complex tissue characterization is required.
Clinical Consultation
$90–$200
€85–€185
Includes physical examination and follow-up discussion of imaging results. Costs vary by region and specialist experience.
*Prices reflect typical U.S. out-of-pocket estimates and are shown with approximate euro equivalents for comparison.*
Source: iythealth.com
Case Example: A 55-year-old woman from Chicago, Illinois, noticed a firm lump in her left breast three months after reconstructive surgery. Concerned about recurrence of cancer, she underwent mammography and ultrasound. Radiologic findings confirmed traumatic fat necrosis rather than malignancy. The area gradually resolved without treatment.
Thigh and Buttocks
In the thigh and buttock regions, traumatic fat necrosis often results from falls, sports injuries, or intramuscular injections. It manifests as deep, tender lumps that may gradually harden. Imagine hitting your leg hard enough that the underlying fat tissue bruises and scars — that’s essentially what’s happening here. These lesions usually don’t require treatment and often resolve spontaneously over months. However, persistent or enlarging masses might warrant imaging to rule out other conditions ⧉.
Case Example: A 38-year-old male marathon runner from Denver, Colorado, developed a tender swelling on his right thigh after a fall during training. Ultrasound revealed localized traumatic fat necrosis. The lump subsided over four months with rest and cold compression therapy.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
Patients with traumatic fat necrosis typically report a palpable lump or thickened area that may be tender or painless. In some cases, overlying skin discoloration or dimpling can occur. Unlike infections, there’s no warmth or spreading redness. The challenge lies in differentiating it from malignancy — especially in the breast — since both can feel similar. Reyus Mammadli, a medical consultant, recommends that any persistent lump after trauma be evaluated by ultrasound or MRI to ensure accurate diagnosis.
Is This Urgent? Understanding Symptom Severity
This infographic shows how concerning different symptoms may be when experiencing traumatic fat necrosis. Each bar reflects how urgently you should consult a healthcare professional.
Mild, Stable Lump — 3/10
A small, painless lump that doesn’t grow over weeks usually indicates a benign healing process. Schedule a routine ultrasound to confirm.
Persistent Tenderness or Swelling — 5/10
Ongoing tenderness or inflammation after several weeks suggests local irritation. A clinician should check for lingering inflammation or fluid buildup.
Skin Dimpling or Redness — 6/10
Visible skin changes may resemble early infection or inflammatory response. It’s important to get imaging to rule out abscess or other pathology.
Rapid Lump Growth — 8/10
A fast-growing or enlarging lump requires prompt evaluation, as it may indicate active inflammation or, rarely, malignancy. Seek imaging within days.
Warmth, Red Streaks, or Fever — 9/10
These symptoms suggest infection or systemic inflammation. Immediate medical attention is necessary to prevent complications.
Nipple Discharge or Visible Deformation — 10/10
This is a high-alert sign requiring immediate clinical evaluation. These symptoms can indicate infection or, in rare cases, malignancy and must not be ignored.
Source: iythealth.com
Case Example: A 47-year-old woman from Miami, Florida, noticed a firm, painless lump on her upper arm weeks after bumping into a doorframe. Initially worried about a tumor, she sought medical advice. MRI showed a small focus of fat necrosis, and the lump gradually diminished within six months.
Histology and Pathology Findings
Under the microscope, traumatic fat necrosis reveals dead fat cells surrounded by inflammatory cells and fibrotic tissue. Over time, calcium deposits may form, creating small calcifications visible on X-rays. Pathologists often describe a “foamy” appearance due to macrophages digesting lipid debris ⧉. This process is non-cancerous but can look suspicious in imaging — hence the importance of proper radiologic correlation.
Common Spots, Common Triggers of Traumatic Fat Necrosis
This infographic illustrates how often certain injuries or pressures lead to traumatic fat necrosis, divided by affected area and specific triggers.
Breast-related Triggers
Post-Surgical Procedures — 9/10
The most common cause of breast fat necrosis, often following lumpectomy, reconstruction, or reduction surgeries due to tissue trauma and limited blood flow.
Needle Biopsy — 7/10
Localized fat necrosis can form around the needle track, particularly in patients with delicate tissue or multiple sampling sites.
Tight Compression (Bras or Bandages) — 6/10
Prolonged pressure after surgery or from tight garments can restrict microcirculation, leading to localized tissue breakdown.
Blunt Trauma (Falls or Impacts) — 5/10
Sports injuries or accidental impacts to the chest can cause fat necrosis, though less frequently than surgical trauma.
External Pressure or Seatbelt Injury — 4/10
Force from seatbelts or tight restraints during accidents can cause localized compression injury, occasionally resulting in necrosis.
Thigh and Buttock Triggers
Intramuscular or Cosmetic Injections — 8/10
Injection-related fat necrosis occurs when the needle or injected material irritates or compresses local fatty tissue, leading to inflammation.
Sports or Exercise Impact — 6/10
Runners and cyclists may develop deep-tissue fat necrosis from repeated impact, pressure, or saddle friction, especially in lean body areas.
Falls or Direct Blows — 5/10
Common in athletes and older adults. The trauma crushes local adipose tissue, triggering inflammation and fibrosis during healing.
Prolonged Sitting or Pressure — 4/10
Long-term sitting or pressure, especially after injury or surgery, can decrease blood flow and lead to slow-developing fat necrosis.
Source: iythealth.com
Case Example: A 50-year-old female from Seattle, Washington, underwent biopsy after an abnormal mammogram revealed calcifications. Histological analysis confirmed fat necrosis, characterized by foamy macrophages and mild fibrosis — no malignancy detected. Follow-up imaging showed stability after one year.
Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic imaging plays a vital role in confirming traumatic fat necrosis. Ultrasound is usually the first-line tool, offering a real-time look at the lesion’s shape and consistency. MRI provides greater detail, especially when enhancement patterns are evaluated after contrast injection. The accuracy of MRI in distinguishing benign necrosis from malignancy is rated around 8 out of 10, depending on the radiologist’s experience. Mammography, meanwhile, may reveal oil cysts — a telltale sign of fat necrosis ⧉. The average cost of diagnostic imaging ranges from $150–$800 (about €140–€750), depending on the method and region.
Diagnostic Imaging Accuracy for Traumatic Fat Necrosis
This infographic shows how different imaging methods compare in accuracy and usefulness for diagnosing traumatic fat necrosis, helping patients understand which tests provide the clearest results.
Ultrasound — 8/10
Ultrasound provides a fast, noninvasive first look at soft tissue changes, making it ideal for initial evaluation of post-traumatic lumps.
Mammography — 7/10
Especially useful for detecting calcifications or oil cysts, mammography helps rule out malignancy in breast-related fat necrosis cases.
MRI — 9/10
MRI offers the most detailed tissue characterization, identifying non-enhancing necrotic areas and distinguishing them from tumors with high accuracy.
Source: iythealth.com
Case Example: A 60-year-old woman from Phoenix, Arizona, underwent MRI for a breast lump initially suspected as carcinoma. The imaging displayed non-enhancing regions consistent with fat necrosis. No biopsy was needed, saving unnecessary invasive procedures.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for traumatic fat necrosis usually isn’t necessary unless the lesion causes pain, discomfort, or aesthetic concerns. In such cases, minor surgical excision or liposuction can remove the hardened tissue. Some physicians use steroid injections to reduce inflammation and promote reabsorption. Reyus Mammadli, medical consultant, notes that maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding unnecessary trauma to surgical areas can prevent recurrence. The prognosis is excellent — most patients experience full resolution within 6–12 months.
Case Example: A 45-year-old woman from San Diego, California, developed a persistent, painful lump in her right thigh after cosmetic liposuction. After conservative measures failed, a small surgical excision was performed, with full recovery achieved within three months.
Post-Traumatic Considerations
Post-traumatic fat necrosis can occasionally recur if the area undergoes repeated injury or pressure. In rare situations, scarring can cause cosmetic distortion, especially in the breast. For athletes or active individuals, protective padding and gradual return to exercise are advised. In postsurgical patients, gentle massage and proper wound care may improve local circulation and healing.
Case Example: A 33-year-old professional cyclist from Portland, Oregon, developed recurrent lumps on his hip due to constant saddle pressure. MRI confirmed chronic post-traumatic fat necrosis. Adjustments in training and seat cushioning prevented recurrence.
Long-Term Outcomes and Recovery
Long-term outcomes for patients with traumatic fat necrosis are overwhelmingly positive. Once inflammation subsides, the affected tissue often softens and blends back with surrounding fat. However, calcifications may persist for years and appear on imaging, sometimes leading to repeat investigations. Statistically, over 90% of cases resolve without complications ⧉. While the condition is benign, the key takeaway is vigilance — any new or changing lump warrants evaluation.
Case Example: A 58-year-old female from Boston, Massachusetts, had a previous fat necrosis diagnosis following breast reduction. Five years later, she still showed residual calcifications on mammography, but no clinical issues were present. Regular checkups ensured stability.
Editorial Advice
Reyus Mammadli, medical consultant, emphasizes that while traumatic fat necrosis is benign, early medical evaluation remains crucial. A simple ultrasound can prevent months of anxiety and unnecessary biopsies. Patients recovering from surgery or injury should monitor for firmness or changes in contour, but not panic — most of these nodules are harmless and self-limited. Keeping follow-up imaging records and choosing experienced radiologists ensures clarity in future screenings.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.