For the majority of people, the most safe type of potassium supplement remains in a multivitamin. Multivitamins include no greater than 99 mg potassium, a tiny fraction of the Recommended Daily Allowance for this mineral. While medicinal preparations frequently are available in the type of potassium chloride, a lot of multivitamins contain potassium citrate, which is potassium salt from citric acid.
Besides potassium citrate and chloride, you can also find this mineral through potassium aspartate, potassium bicarbonate, potassium gluconate and potassium orotate.
Types of Potassium Supplements
Potassium levels in the body need to be carefully handled to avoid complications that occur with high or low levels. Potassium supplements might be appropriate if your body lacks this nutrient. A number of different types of potassium supplements are offered. The cause of potassium shortage identifies what type of potassium supplement is the best option.
Indicators for Potassium Supplement Use
Potassium is a mineral and electrolyte that is vital to the function of the heart, muscles, nerves, kidney and digestive system and is saved primarily within the cells of the body. Low potassium levels, known as hypokalemia, might be caused by conditions of malabsorption, alcoholism (don’t consume alcohol, alcohol is harmful for health), diarrhea, vomiting, extreme sweating and use of particular medications referred to as loop diuretics.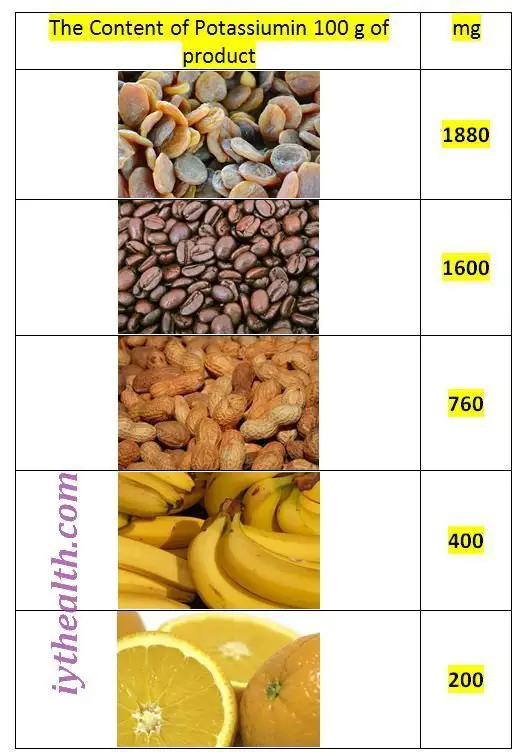
Hypokalemia must be carefully kept an eye on, and supplements need to only be started under the guidance of a doctor. Potassium supplements might not be proper for older adults, individuals with declined kidney function and people taking certain medications.
Selecting the Appropriate Supplement
Your doctor will recommend or recommend the type of supplement that is suitable for the cause of potassium shortage. Potassium salts include potassium chloride, phosphate, bicarbonate, gluconate, citrate, aspartate and orotate. Potassium chloride is effective in treating most causes of potassium deficiency. Many potassium from food is bound to phosphate, so increased potassium consumption will not help to correct potassium shortage that relates to chloride deficiency.
Potassium chloride might be the best choice for hypokalemia from use of diuretics or from vomiting, or from the use of alkalizing salts such as gluconate, bicarbonate or citrate, which might cause low chloride levels. Potassium bicarbonate might be the best alternative if low potassium takes place along with metabolic acidosis.
Ways to Use Potassium Supplements
Potassium supplements can be found in various kinds consisting of tablets, capsules, powders, liquids and granules. Some forms are produced quick absorption and some forms are meant for slower absorption. Extended release pills and tablets need to be swallowed entire and should not be chewed.
Powders, liquids, granules and effervescent tablets are generally dissolved in water. All kinds of potassium supplement must be taken with appropriate fluid to prevent stomach inflammation. Potassium supplements must be used only as directed on the label and in the dose prescribed by a doctor.
How Much Potassium Do You Need a Day
Inning accordance with the Food and Nutrition board, adults need 4,700 milligrams of potassium daily. The amount of potassium required from a supplement needs to take into consideration the level of deficiency and the quantity of potassium consumed in the diet. Vegetables and fruits are the richest sources of potassium.
The quantity of supplement required depends upon the strength of the supplement. Follow instructions from your doctor and the supplement label to determine how much to take. Oral dosages of more than 18 grams may cause severe reactions due to high potassium levels, referred to as hyperkalemia.
Reactions to Potassium Supplements
In some circumstances, individuals might have adverse responses to potassium supplements. Normally these reactions involve intestinal distress such as nausea, diarrhea, vomiting and sometimes intestinal tract ulcers. The most severe unfavorable reaction to potassium supplements is hyperkalemia, which is defined by tingling in the hands and feet, unusual heart rhythm, muscle weakness and sometimes heart attack.
Potassium Supplements: Does Type Affect Absorption?
Diet is without a doubt the best source of potassium. A number of the foods rich in potassium likewise contain a variety of nutrients vital to your health. Beyond diet, potassium supplements are offered, however you should use them just when directed to do so by a doctor. Your everyday multivitamin might include small, safe quantities of potassium, however large dosages of extra potassium can cause dangerous side effects, so do not self-prescribe this vital mineral.
Absorption
The best kind of potassium for absorption isn’t really relevant. Dr. Elson Haas, discusses that potassium is normally well absorbed in your small intestine. In truth, approximately 90 percent of consumed potassium is absorbed during the process of food digestion. You need not pick a particular form of this mineral to guarantee absorption and assimilation. That being stated, your doctor will tell you which form is best matched to your requirements.
Daily Potassium Intake
The suggested dietary intake of potassium is set at 2,000 mg daily, according to the University of Maryland Medical Center. Your diet likely fulfills this requirement. A lot of meat, such as beef, chicken and turkey, include potassium. It’s likewise discovered in cod, flounder, salmon and sardines. You likewise get potassium from tomatoes, potatoes, sweet potatoes, broccoli, peas, lima beans, bananas, cantaloupe, kiwi, apricots and nuts. Even milk, yogurt and peanut butter are rich in potassium, so examine your diet to figure out how much potassium you’re taking in every day.
Potassium Deficiency
A shortage is seldom caused by a lack of potassium in your diet. You’re much more likely to develop hypokalemia– or low potassium– from extended bouts of diarrhea or vomiting in addition to eating disorders, kidney failure, extreme sweating and using laxatives or diuretics. Symptoms of hypokalemia don’t normally manifest till serum potassium drops well listed below the advised level, which is 3.6 to 4.8 mEq/L. When this happens, a supplement will not likely help, and a medical professional should administer it intravenously.
Side Effects of Potassium Intake
Warning
According to the University of Maryland Medical Center, potassium supplements need to only be taken under the guidance of a doctor. Supplemental potassium can cause undesirable side effects such as nausea, diarrhea and stomach inflammation. Taking too much can cause a harmful condition called hyperkalemia, which might cause irregular heart rhythms, slowed heart beat and muscle weakness.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.







