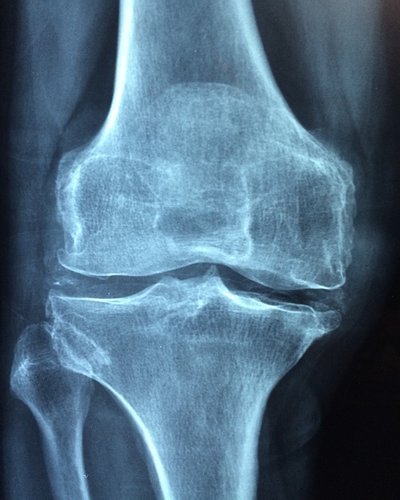
Osteoarthritis (OA) affects more than one-third of adults over the age of 65. A considerable fraction of younger adults likewise struggle with OA symptoms.
Osteoarthritis Causes
OA takes place when cartilage starts to break down from age or heavy use. Cartilage normally covers the ends of bones and enables them to move freely against each other.
The degeneration of cartilage exposes the bones of the joint and permits bone-on-bone contact. This can cause:
- pain
- tightness
- reduced variety of movement
- changes in joint look.
Osteoarthritis can affect any joint in your body, but the most commonly impacted areas are:
Health Support: High-absorption Magnesium Glycinate is often used for muscle, sleep, and metabolic support. You can find this supplement on Amazon here.
- hands
- hips
- knees
- neck
- lower back.
Not all joint pain and tightness is caused by OA. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can cause comparable pain, however there are a number of physical findings that distinguish RA, an inflammatory disease, from OA. One easily noticeable difference is that RA, unlike OA, is usually in proportion. If it affects a joint on one side of the body, it will generally impact the same joint on the other.
Common Osteoarthritis Symptoms
The symptoms of OA differ from person to person. Some individuals may just have mild pain and swelling. Others may experience joint damage that significantly impacts their lifestyle. OA of the knees, in certain, is a major cause of disability in the United States.
Tightness
For many people with OA, tightness is generally even worse in the early mornings. It is normally also worse after extended periods of lack of exercise or rest. At these times, joints may feel:
- achy
- rigid
- hard to move.
Pain
Discomfort and aching pain are common symptoms of OA. Muscle pain can likewise take place in the surrounding tissue. Normally, pain, like stiffness, is most intense after sleep or a period of inactivity.
Some people with OA feel more pain during movement of the joints and less pain when at rest. With time, the pain may occur even when the joints are not used.
Joint inflammation, sensitivity of the joints to touch, can also take place in individuals with OA.
Pain and inflammation can be caused by:
- bones rubbing versus each other
- inflammation in the joints
- bone stimulates (bony growths)
- pinched nerves caused by swelling and displacement of joint tissue.
Swelling
Swelling is more typical in people with RA than OA. However, individuals with OA likewise experience swelling. Swelling is the body’s reaction to irritants, such as bone-on-bone contact. It contributes to the tightness and pain experienced by patients with OA.
Loss of Flexibility and Range of Motion
According to the CDC, about 80 percent of individuals with OA have some problem with range of movement. A quarter need help with daily living activities. They may require help with:
- dressing
- bathing
- putting on shoes
- entering and out of chairs
- climbing up stairs.
Bone Spurs
Bone stimulates are small bony forecasts. They can take place naturally, however they may also be a response to inflammation in a joint. Bone stimulates, also called osteophytes, can at some point be felt as hard little lumps around joints impacted by OA. Nevertheless, bone stimulates can rub versus neighboring nerve and bone, triggering added pain.
Fatigue
Individuals with OA frequently need to put in extra physical effort in order to carry out the fundamental everyday jobs of living. This can cause fatigue.
Inflammation is caused by chemical arbitrators called cytokines. These can likewise cause fatigue.
Noisy Joints.
Lots of people with OA hear sounds in their joints when they move. Their joints may bang such as:
- creaking
- snapping
- crackling
- grinding.
These sounds are frequently accompanied by discomfort or pain.
Depression and/or Anxiety
People who experience OA are at an increased risk for anxiety and depression. Chronic pain from OA can cause a large amount of stress, as can the disability that typically arises from OA.
Having healthy coping systems in place can reduce the risk of depression and anxiety caused by OA.
Fever
Fever is not usually a symptom of OA. Nevertheless, comprehensive inflammation can cause a low-grade fever.
Joint Symptoms That Signal an Emergency
OA might negatively impact your quality of life. However, it is normally not a disease that requires immediate or emergency action.
That said, not all joint pain is caused by OA. Joint pain can also be caused by other, serious health issue. Call your doctor if you experience:
- joint pain lasting longer than three days
- severe, unusual joint pain
- severe swelling in a joint
- problem moving the joint
- heat or soreness in the skin around the joint
- fever or unusual weight loss.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.