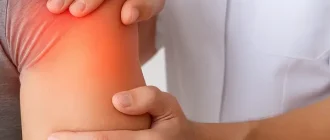
Soft tissue damage is a form of injury that impacts the muscles, tendons, and ligaments. This particular injury can be attributed to a variety of activities, including athletic pursuits, physical exertion, and routine daily tasks. Soft tissue injuries may be categorized as either acute injuries or overuse injuries. Acute injuries are a result of sudden trauma, whereas overuse injuries develop gradually over a period of time. In this guide, we shall present factual information on soft tissue damage, its prevention, and treatment.
Types of soft tissue damage
There exist various forms of soft tissue injury, such as sprains, strains, contusions, tendinitis, bursitis, and stress fractures. A sprain is a medical condition that involves the stretching and/or tearing of a ligament. Ligaments are fibrous connective tissues that serve to connect bones to one another, thereby providing joint stability. On the contrary, a strain is an injury to the muscle and/or tendon. Tendons represent fibrous cords of tissue which serve to attach muscles to bones.
Contusions are a result of direct impact or repeated impacts by a blunt object on a specific area of the body. This is an injury that involves the compression of the underlying muscle fibers and connective tissue, without any visible breakage of the skin. Tendinitis and bursitis are frequently encountered soft-tissue injuries that arise due to inflammation resulting from overuse injuries or direct joint trauma. Finally, stress fractures refer to minor fissures in a bone that frequently arise in weight-bearing bones located in the lower extremities.
Causes
Soft tissue injuries may arise due to various factors, such as overuse, trauma, or direct impact. Although such injuries are frequently encountered, they can elicit discomfort and necessitate appropriate medical attention to guarantee complete recuperation. It is imperative to acquire a more comprehensive comprehension of soft tissue damage, its prevention, and treatment.
| Body Area | Reason for Soft Tissue Injuries |
|---|---|
| Knee | Most commonly injured joint due to its complex structure, commonly affected by overuse, impact injuries, and falls |
| Shoulder | Complex structure and high mobility, prone to overuse and impact injuries such as dislocations and sprains |
| Ankle | Frequently injured joint during high-impact activities such as running and jumping |
| Hamstring | Prone to strains during high-intensity activities, not enough stretching before exercise or fatigue |
| Lower Back | Commonly affected due to poor posture, overuse and heavy lifting during work and exercise |
| Wrist | Small joint, susceptible to overuse injuries such as repetitive strain and sprains during activities like sports |
How to avoid
The optimal approach to evade soft tissue injury is to implement preventive measures. It is imperative to engage in a thorough warm-up prior to exercising, utilizing appropriate equipment, and incorporating rest days in between workouts to mitigate the risk of overuse injuries. It is imperative to employ appropriate techniques while engaging in athletic pursuits, such as weightlifting, cycling, or any other activity that places additional stress or strain on the body.
Treatment
In the event of a soft tissue injury, there are various measures you can undertake to facilitate your recuperation. It is imperative to immediately cease the activity that led to the injury. It is recommended to apply ice to the affected area for 20 minutes at a time, multiple times throughout the day. It is imperative to refrain from the direct application of ice onto the skin, as it may result in exacerbation of the injury. I recommend utilizing cold packs to alleviate swelling and inflammation. Wearing an elastic compression bandage aids in the prevention of further swelling through compression. Finally, please elevate the affected region above your heart while at rest in order to decrease swelling.
It is imperative to obtain medical attention when deemed necessary. With appropriate preventive and therapeutic interventions, it is possible to recuperate from soft tissue injury and resume an active and healthy way of life.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.