Some women will craft hemorrhoids during pregnancy. Hemorrhoids may improve in a few days without treatment, or they may require treatment in your doctor’s workplace. Dietary changes can help treat and avoid hemorrhoids.
What are Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins around your anus or lower anus. Hemorrhoids can be internal or external. Internal hemorrhoids are within the anus. External hemorrhoids are beyond the anal opening. Hemorrhoids can sometimes hurt or itchy. They can also bleed during defecation.
Hemorrhoids are very common. Seventy-five percent of individuals will have hemorrhoids at some time. Hemorrhoids are more common in individuals in between the ages of 45 and 65.
How Long Do Hemorrhoid Symptoms Last?
If your hemorrhoids are small, your symptoms may clear up in a few days without treatment. You might likewise have to make simple diet and lifestyle changes.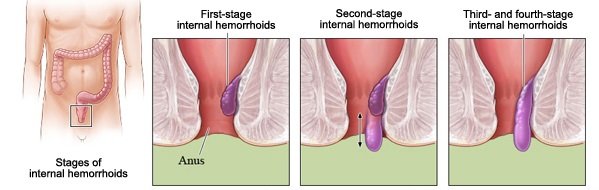
Some internal hemorrhoids become so bigger that they stand out of the rectum. These are called prolapsed hemorrhoids. Prolapsed hemorrhoids can take longer to heal and might need treatment from a doctor.
Some women will develop hemorrhoids during pregnancy. This is due to the fact that the increased pressure in your abdomen, specifically in the 3rd trimester, may make the veins in your anus and rectum larger. Pregnancy hormones might likewise make it more likely for your veins to swell. If you craft hemorrhoids during pregnancy, your symptoms might last up until you give birth.
How To Know If You Have Hemorrhoids?
How to know if you have an internal hemorrhoid? You may have no visible symptoms from internal hemorrhoids. Sometimes, a bowel movement might aggravate an internal hemorrhoid and cause bleeding. If the internal pile is pushed beyond your anal opening, you may have bleeding during defecation and symptoms in the anal area that include:
- itching
- burning
- discomfort
- pain
- a lump
- swelling.
So, signs and symptoms of hemorrhoids typically depend on the type of hemorrhoid.
External hemorrhoids
These are under the skin around your rectum. Symptoms and signs may consist of:
- Itching or inflammation in your anal region
- Pain or discomfort
- Swelling around your anus
- Bleeding
Internal hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids lie inside the anus. You typically can’t see or feel them, and they hardly ever cause discomfort. However straining or irritation when passing stool can cause:
- Pain-free bleeding during bowel movements. You may notice percentages of bright red blood on your toilet tissue or in the toilet.
- A hemorrhoid to press through the anal opening (prolapsed or extending hemorrhoid), leading to pain and irritation.
- Thrombosed hemorrhoids
If blood pools in an external hemorrhoid and forms a clot (thrombus), it can result in:
- Extreme pain
- Swelling
- Inflammation
- A hard lump near your rectum
What Can You Take for Relief?
If you have hemorrhoids, lifestyle changes might help them heal much faster. One cause of hemorrhoids is straining during bowel movements. Adding more high-fiber foods to your diet, such as veggies, fruits, and entire grains, can help soften your stool and make it simpler to pass. You ought to likewise drink lots of water to help alleviate constipation and reduce straining during defecation.
Here are some extra things that may help relieve symptoms:
- Reduce the time you rest on the toilet.
- When you feel the urge to move your bowels, go as quickly as possible.
- Put your feet on a small stool during defecation to change the position of your rectum.
- If you’re pregnant, sleep on your side. This will help relieve some of the pressure around your anus.
- Ask your doctor about taking a fiber supplement, such as psyllium (Metamucil) or methylcellulose (Citrucel). A tablespoon of mineral oil added to food can likewise help soften stools.
- Keep the anal area tidy. Take regular showers, and use damp wipes to clean up the area around your rectum after you pass a defecation.
- Use a sitz bath or sit in a warm tub for a few minutes to bathe the anal area.
You may likewise attempt using non-prescription (OTC) topical medications to relieve discomfort, such as phenylephrine hemorrhoidal gel (Preparation H). These products are used if the hemorrhoids are bulging and inflamed. Limitation use of products which contain steroids due to the fact that long-term use may cause thinning of the skin around the anus. If OTC medications aren’t assisting, talk with your doctor to see if you require extra treatment.
What are Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids?
Small hemorrhoids often improve without treatment or with home treatment and lifestyle changes. If you’ve continued problems or complications, such as bleeding, you must see your doctor. Your doctor can eliminate other causes of bleeding during defecation, such as colon or anal cancer. If your symptoms become severe, your doctor might suggest medical procedures to get rid of or diminish the hemorrhoids.
Your doctor may advise a minimally invasive outpatient treatment. Outpatient treatments are treatments that your doctor carries out in their office. Some treatments include the following:
- Rubber band ligation is the most common nonsurgical treatment, and it includes your doctor tying a tight band around the base of the pile to cut off the blood supply. Eighty percent of individuals who receive treatment for hemorrhoids have this type of treatment.
- During coagulation, your doctor uses infrared light, heat, or severe cold to diminish the hemorrhoid.
- During sclerotherapy, your doctor injects a chemical to diminish the pile.
If you have severe hemorrhoids or hemorrhoids that don’t respond to in-office medical treatments, you may require a doctor to surgically extract them. This has actually been shown to provide symptom relief and reduce future outbreaks.
What are the Risk Factors for Hemorrhoids?
The risk factors for hemorrhoids are primarily associated to increased pressure on the anal and rectal veins. A family history of hemorrhoids might increase your risk. The risk factors include:
- age
- pregnancy
- weight problems
- frequent constipation or diarrhea
- investing too long resting on the toilet
- not having enough dietary fiber
- overusing enemas or laxatives
- straining during defecation.
Will Your Hemorrhoids Return?
When you’ve had hemorrhoids, they can return. Scientists have not carried out many research studies on the rate of reoccurrence. Scientists in one study in 2004 compared the rate of recurrence of hemorrhoids in 231 individuals. Some of the study participants got treatment at home, and others had surgery to eliminate their hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids recurred in 6.3 percent of the people who had surgery and in 25.4 percent of the people who got at-home treatment.
Tips for Prevention
Changes in diet and your everyday regimen can help keep hemorrhoids from returning. Home treatments to ease hemorrhoid symptoms can likewise prevent future flare-ups. Follow these suggestions:
- Eat the advised amount of high-fiber foods and drink a lot of fluids to keep your stools soft and prevent straining during defecation.
- Exercise routinely, which will help keep your bowel movements on a more routine schedule.
- If you’re obese, slim down to reduce the pressure on the veins in your anus and anus.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.