Doctors have no idea why some people experience allergic reactions. Allergic reactions appear to run in families and can be acquired. If you have a close family member who has allergic reactions, you’re at higher risk for developing allergies.
What Causes an Allergic Reaction?
Although the reasons allergic reactions establish aren’t understood, there are some substances that typically cause an allergic reaction. People who have allergies are generally allergic to several of the following:
- animal dander
- bee stings or bites from other insects
- particular foods, including nuts or shellfish
- specific medications, such as penicillin or aspirin
- specific plants
- pollen or molds.
What are the Symptoms of an Allergic Reaction?
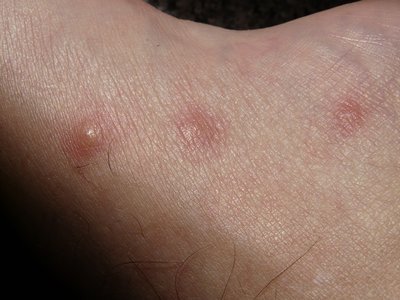
The symptoms of an allergy can differ from mild to severe. If you end up being exposed to an allergen for the first time, your symptoms may be mild. These symptoms might worsen if you repeatedly enter into contact with the irritant.
Symptoms of a mild allergy can include:
- hives (itchy red spots on the skin)
- itching
- nasal blockage (called rhinitis)
- rash
- scratchy throat
- watery or itchy eyes.
Severe allergic reactions can cause the following symptoms:
- abdominal cramping or pain
- pain or tightness in the chest
- diarrhea
- problem swallowing
- dizziness (vertigo)
- worry or anxiety
- flushing of the face
- queasiness or vomiting
- heart palpitations
- swelling of the face, eyes, or tongue
- weakness
- wheezing
- trouble breathing
- unconsciousness.
A severe and abrupt allergic reaction can establish within seconds after exposure to an irritant. This type of response is called anaphylaxis and results in lethal symptoms, consisting of swelling of the respiratory tract, inability to breathe, and an abrupt and severe drop in blood pressure. If you experience this type of allergic reaction, seek instant emergency situation help. Without treatment, this condition can lead to death within 15 minutes.
How is an Allergic Reaction Identified?
Your doctor can identify allergic reactions. If you experience symptoms of an allergic reaction, your doctor will perform a test and ask you about your health history. If your allergies are severe, your doctor might ask you to keep a journal that details your symptoms and the substances that appear to cause them. Your doctor may wish to buy tests to identify what’s triggering your allergy. The most frequently bought types of allergic reaction tests are:
- skin tests
- obstacle (elimination-type) tests
- blood tests.
A skin test involves using a small amount of a thought allergen to the skin and watching for a reaction. The substance might be taped to the skin (patch test), applied via a small prick to the skin (prick test), or injected just under the skin (intradermal test). A skin test is most important for detecting:
- food allergy.
- mold, pollen, and animal dander allergic reaction.
- penicillin allergic reaction.
- venom allergy (such as mosquito bites or bee stings).
- allergic contact dermatitis (a rash you receive from touching a compound).
Difficulty screening is useful in identifying food allergic reactions. It includes getting rid of a food from your diet for a number of weeks and looking for symptoms when you eat the food once again.
A blood test for an allergy checks your blood for antibodies against a possible irritant. An antibody is a protein your body produces to eliminate hazardous substances. Blood tests are an alternative when skin testing isn’t really useful or possible.
See also: What You Should Know About Genetically Modified Foods?
How is an Allergic Reaction Treated?
If you experience an allergic reaction and you have no idea what’s causing it, you might need to see your doctor to identify what the cause of your allergy. If you have a known allergy and experience symptoms, you might not have to look for medical care if your symptoms are mild. In most cases, over-the-counter antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl), can be efficient for controlling mild allergic reactions.
If you or someone you understand experiences a severe allergy, you ought to look for emergency medical attention. Check to see if the person is breathing, call 911, and provide CPR if needed. People with known allergies frequently have emergency situation medications with them such as an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen). Epinephrine is a “rescue drug” due to the fact that it opens the airways and raises blood pressure. The person might need your help to administer the medication. If the person is unconscious, you need to:
- Lay the individual flat on their back.
- Elevate the individual’s legs.
- Cover the individual with a blanket.
This will help avoid shock.
What is the Long-lasting Outlook?
If you have a recognized allergic reaction, preventing an allergy will enhance your outlook. You can avoid these responses by avoiding the allergens that impact you. If you have serious allergies, you should always carry an epinephrine auto-injector and inject yourself if symptoms happen.
Your outlook will also depend upon the seriousness of your allergy. If you have a mild allergy and look for treatment, you will have a great chance for recovery. However, symptoms may repeat if you enter into contact with the irritant once again. If you have a severe allergy, your prognosis will depend on receiving fast emergency care. Anaphylaxis can result in death. Prompt medical care is necessary to enhance your result.
How can You Avoid an Allergy?
As soon as you identify your allergic reaction, you can:
- Avoid direct exposure to the irritant.
- Look for treatment if you are exposed to the irritant.
- Bring medications to treat anaphylaxis.
You might not have the ability to avoid an allergy totally, however these steps can help you to avoid future allergies.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.






