Crohn’s disease is a condition that can affect the entire digestive system, consisting of the colon, small intestine, or big intestine. Typically, the end of the small intestine (the ileum) is characteristically affected. It’s characterized by stomach pain, diarrhea, or other serious digestive symptoms caused by inflammation.
What is Crohn’s Disease?
Crohn’s disease is a serious condition. Left untreated, it might cause digestive tract scarring (stenosis), fistulas, obstruction in the bowels, ulcers or colon cancer. In serious cases, Crohn’s disease can be life threatening. There is no recognized cause or treatment for Crohn’s disease. With treatment, you can expect to live a regular life.
Typical symptoms of Crohn’s disease include:
Health Support: This Vitamin K2 + D3 Complex is essential for bone density, cardiovascular health, and immune function. It’s a highly-rated formula for those looking to maintain optimal nutrient levels. You can find it on Amazon.
- diarrhea
- stomach pains
- cramping
- bloody stool
- ulcers
- weight loss
- loss of appetite
- poor nutrition
- fever
- tiredness.
How to Test For Crohn’s Disease
To identify Crohn’s disease, your doctor will first do a full examination to dismiss other conditions. There’s no easy method to identify Crohn’s, so your doctor should first identify what is triggering your symptoms. Because of this, it can take a very long time to lastly get a diagnosis of Crohn’s disease. There are a number of tests that can be used to detect this condition.
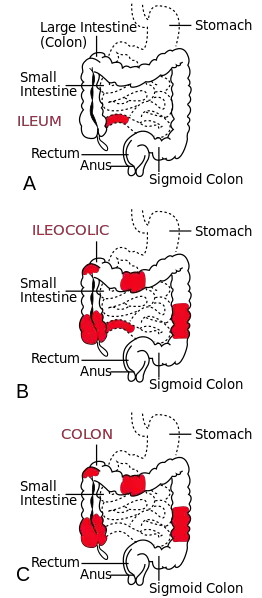
The primary tests for Crohn’s disease include imaging tests. Your doctor will need to be able to see what’s going on with your digestive tract to make the diagnosis. Some tests show imaging from the externally, like x-rays, and others involve analyzing the bowel with an endoscope for direct visualization and using a camera, during the procedure, to record any abnormalities.
Typically a biopsy of the tissues is likewise carried out. Because Crohn’s disease can affect numerous locations in the digestive tract and most tests have particular protection areas, more than one type of test is generally needed.
Stool Tests
Stool tests can be used to search for blood. Blood in the stool signifies a digestive condition, like Crohn’s. To do a stool test, you will have to supply a sample to your doctor. The sample will be sent to a laboratory for testing. They will try to find signs of blood or other irregularities. This test might be uncomfortable, however it shouldn’t be painful or have any side effects.
Health Support: This high-absorption Magnesium Glycinate (200 mg) is gentle on the stomach and supports muscle relaxation, better sleep, and metabolic health. You can find this trusted formula on Amazon.
Blood Test
Blood tests can be used to search for infection or antibodies in the blood. Having antibodies does not indicate you have Crohn’s. Blood tests can show an increased level of white blood cells or platelets in the blood. An increase in these levels could imply inflammation in the body. Inflammation might mean Crohn’s or other inflammatory diseases. Blood tests would never ever be used as the only test for Crohn’s. Other tests and a biopsy would most likely be required.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests include X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computerized tomography (CT) scan. These images are used to see the digestive tract from the outside. They help your doctor see the tissues and document any damage or inflammation. Often focused on the small intestine, imaging tests could likewise include the stomach or colon. Often your doctor will have you drink a solution called barium that causes contrast on the photos.
This permits your doctor to see variation in tissues beyond the protection area of other tests. One specific test, called the upper GI series, consists of a range of imaging tests created to obtain a total photo of the small intestine. The CT scans or MRI show more tissues that other tests do not expose. This helps determine the location of the inflammation. This test likewise helps identify potentially serious complications from the disease, like fistulas or abscesses.
Biopsy
Biopsy includes taking a small tissue sample for testing. Frequently the sample is collected during another test, like a colonoscopy. The sample is then sent out to a lab for screening of the tissues. The lab will look for signs of inflammation or other problems with the tissues. Biopsies help confirm what was seen during an endoscopy or imaging tests.
Endoscopy
Endoscopy is a test where a thin, versatile tube is inserted through the rectum to take a look at the inner walls of the colon. Colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy are types of endoscopy. With endoscopy, a sample can be gathered for additional testing. In some cases individuals have small groupings of cells (granulomas) in the colon that can only be seen with a colonoscopy. Granulomas typically indicate Crohn’s.
The disadvantage of colonoscopy is that it’s an uncomfortable and invasive procedure. The benefit is that its one of the few tests that permit doctors to see the inside of the colon. With this procedure, they can even imagine the area between the small intestine and colon where damage from Crohn’s disease is frequently seen. Your doctor can see the whole colon with a colonoscopy. Sigmoidoscopy resembles a colonoscopy, however, with this procedure, your doctor can just analyze at the end (distal) part of the colon.
Capsule Endoscopy
Capsule endoscopy is a cutting edge test used when other tests aren’t definitive. For a capsule endoscopy, you have to swallow a small pill that has a tiny camera inside. This permits pictures of the within your digestive tract. If the images come back to show some signs of Crohn’s, your doctor may do more screening.
The advantage of a pill endoscopy is that it’s minimally invasive. The pill is created to travel through your digestive tract without triggering discomfort and provide useful imaging to help identify Crohn’s disease or other digestive tract issues. The disadvantage is that it doesn’t take biopsies and just sees into the small intestine. A colonoscopy is still generally done to see the colon.
Treating Crohn’s Disease
There are currently no known treatments for Crohn’s disease. Some treatment options may help reduce the risk of symptom flare-up. The objective of treatment alternatives is to lessen symptoms, prevent complications, and reduce inflammation.
Medications, like anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressive medications, or antibiotics are the main choices for treating Crohn’s disease. Other treatment options include:
- laxatives
- anti-diarrheal medications
- painkiller
- iron supplements
- nutritional therapy or dietary changes
- vitamin B-12 injections
- calcium supplements
- vitamin D supplements.
Reducing stress and keeping your body immune system healthy might likewise help with symptoms.