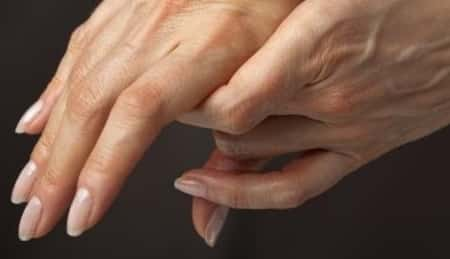
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and potentially long-term damage. Recognizing its early signs is crucial for effective management and prevention of joint damage. But what exactly are these signs, and how can they help with early detection?
Prevalence of RA by Age and Gender
1. Morning Stiffness: A Key Indicator
One of the hallmark symptoms of early RA is stiffness in the joints, especially noticeable in the morning. This stiffness often lasts longer than 30 minutes and can affect daily activities. Unlike the temporary stiffness caused by overuse or injury, RA-related stiffness persists and can worsen over time.
Duration of Morning Stiffness in RA Patients
| Duration | Percentage of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Less than 30 minutes | 30% |
| 30-60 minutes | 45% |
| More than 60 minutes | 25% |
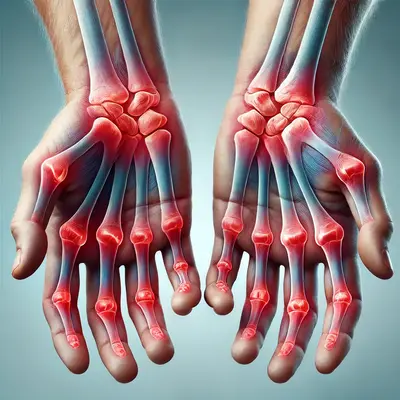
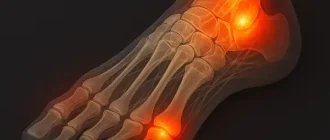
2. Swollen and Tender Joints
RA commonly causes swelling in the small joints of the hands, wrists, and feet. These joints may also feel warm and tender to the touch. Swelling is often symmetrical, meaning if one hand is affected, the other usually is too.
3. Fatigue and General Malaise
Persistent fatigue is a common early symptom of RA. Patients often describe feeling unusually tired or experiencing a general sense of unwellness. Fatigue can occur even before joint pain becomes noticeable.
4. Joint Pain That Comes and Goes
Early RA may present as intermittent joint pain, often described as a dull ache. This pain may initially come and go but tends to become more consistent and severe as the disease progresses.
5. Redness and Warmth in the Joints
Inflammation caused by RA can make the skin around the affected joints appear red and feel warm. This symptom is particularly common in the hands and wrists.
6. Unexplained Weight Loss
Unintended weight loss can occur in the early stages of RA due to systemic inflammation. This symptom often goes unnoticed but may coincide with other signs.
7. Low-Grade Fever
A low-grade fever (below 100°F or 37.8°C) is another subtle sign of RA. It results from the body’s inflammatory response and often accompanies fatigue and joint pain.
8. Difficulty with Daily Activities
Tasks like gripping objects, opening jars, or climbing stairs may become challenging due to joint stiffness and pain. Patients might also notice a decline in their overall hand strength.
Did you know?
RA affects approximately 1.5 million people in the United States alone, with women being three times more likely than men to develop the condition. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly slow its progression. Source
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you experience persistent joint pain, swelling, or other symptoms lasting more than six weeks, it’s time to consult a healthcare provider. Early intervention is key to managing RA effectively and preventing irreversible joint damage.
How Is RA Diagnosed?
RA is diagnosed through a combination of:
- Physical Examination: Checking for joint swelling, tenderness, and range of motion.
- Blood Tests: Identifying markers such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-CCP antibodies.
- Imaging: X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds to detect joint damage and inflammation.
Treatment Options for Early RA
While there is no cure for RA, early treatment can prevent joint damage and improve quality of life. Common treatments include:
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): These medications slow disease progression.
- Biologic Agents: Targeted therapies that block specific inflammatory pathways.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to maintain joint function and reduce pain.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, eating an anti-inflammatory diet, and staying active.
Impact of Early Treatment on Long-Term Joint Damage
| Treatment Timing | Reduction in Joint Damage (%) |
|---|---|
| Treatment Within 6 Months | 70% |
| Treatment After 6-12 Months | 50% |
| Treatment After 12 Months | 30% |
What Makes Early Diagnosis Crucial?
The sooner RA is diagnosed, the more effective treatment will be. Studies show that initiating treatment within six months of symptom onset can lead to better long-term outcomes, including reduced joint damage and improved physical function.
RA Diagnosis Methods: Frequency of Use
Editorial Advice
If you suspect you might have rheumatoid arthritis, don’t wait for symptoms to worsen. Reach out to a healthcare provider as soon as possible. With modern treatments and early intervention, many RA patients live active and fulfilling lives.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.