Any kind of injury that causes a break in the skin can be considered a wound. Most wounds will heal without issue, but some can become infected, leading to more serious health concerns.
Types of Wounds
Wounds can be divided into two categories: open and closed. Open wounds include lacerations, cuts, and punctures and penetrate the skin. Closed wounds, such as bruises and contusions, don’t break the skin.
See also: Fungal Skin Infection
Types of Wound Infections
Wound infections can stem from bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Being aware of the distinct kinds of wound infections and the method to address them can assist you in avoiding future issues.
Bacterial Wound Infections
Bacterial wound infections can develop when bacteria enter into a wound. These bacteria, like Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, can give you this type of infection. Manifestations can include irritation, soreness, agony, and suppuration. Generally, management involves anti-infection agents and injury care.
Fungal Wound Infections
If a wound is exposed to a particular type of fungus, it can lead to a fungal wound infection. Candida albicans and Aspergillus could be the source of the issue, these being types of fungus. It is possible to observe redness, itching, and an unappealing odour as signs of a fungal wound infection. Treatment often entails antifungal medications and wound care.
Viral Wound Infections
When viruses make their way into a wound, viral wound infections can occur. Herpes simplex virus and human papillomavirus are two of the viruses that can cause these infections. The infection may be accompanied by symptoms such as redness, itching, and blisters. It is usually treated with antiviral medications as well as wound care.
Read also about the home remedies for candida skin infection
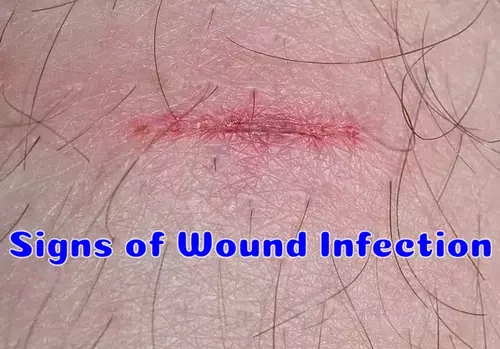
Common Signs of Wound Infections
Wound infections can be serious, so it pays to know their signs. Being aware of the following seven signs of a wound infection can help you spot a problem and seek medical care promptly.
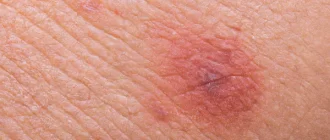
- Redness: The area around the wound may turn red, and it might be warm to the touch in addition to being swollen.
- Pain: Infection can cause pain in the vicinity of the wound, which may range from mild to severe and may worsen over time.
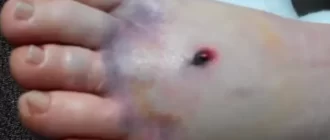
- Drainage: Infected wounds typically produce drainage in the form of a yellow or green fluid that has a bad smell.
- Fever: If the infection is serious, a fever may emerge together with chills and sweat.
- Swelling: Swelling may occur around the wound, and the area may feel tender when touched. It may also be red and warm.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and weak is one of the most common signs of an infection. It may also be difficult to focus on tasks.
- Loss of Appetite: When infected, appetite may drop significantly, and meals may no longer be enjoyable.
If you experience any of these signs of infection, it is important to seek medical attention right away. Your doctor can diagnose the infection and prescribe the right treatment.
See also: Red Itchy Skin Around the Nose
Preventing and Treating Wound Infections
When you suffer a wound, it is essential to take the necessary steps to make sure it doesn’t get infected. Wound infections can be painful and can lead to further health problems if not treated correctly. Here are five steps to help protect your wound and treat any infections that may occur.
- Clean the Wound:
The initial step to preventing a wound infection is to clean the wound thoroughly. Use warm water and soap to clean the wound and get rid of any dirt or debris. If the wound is deep, it may need to be flushed with a saline solution. - Apply Antibiotic Ointment:
When the wound has been cleaned, put on an antibiotic ointment to help stop infection. This will help keep the wound moist and reduce the danger of infection. - Cover the Wound:
Cover the wound with a sterile bandage or dressing to protect it from further contamination. Change the bandage or dressing frequently to maintain the wound clean. - Monitor the Wound:
It is critical to keep an eye on the wound for signs of infection. Look for redness, swelling, pain, or discharge. If any of these signs are present, seek medical attention right away. - Take Antibiotics:
If the wound becomes infected, it is essential to take antibiotics to treat the infection. Follow the instructions of your doctor or healthcare provider to guarantee the infection is treated properly.
By following these five steps, you can take steps to prevent and treat wound infections. Keep in mind to always seek medical attention if you experience any signs of infection.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.