What is calcium shortage disease? Calcium shortage disease, likewise called hypocalcemia, increases the risk of establishing illness like osteoporosis. Symptoms of hypocalcemia can include weak hair, nails, amnesia, and seizures. Taking more than your doctor’s recommended dose of calcium might be deadly.
Calcium is an important mineral. Your body uses it to support blood pressure and construct strong bones and teeth. When you don’t get enough calcium, you increase your risk of developing diseases like osteoporosis, osteopenia, and calcium deficiency disease. You need to consume the suggested amount of calcium daily through the food you eat, supplements, or vitamins.
What Causes Calcium Shortage Disease?
The natural aging procedure can cause calcium shortage disease. The majority of the calcium in your body is kept in your bones. As you age, your bones begin to thin or end up being less thick. This increases your day-to-day calcium requirement.
For children and teenagers, the recommended everyday allowances for calcium are the same for both sexes.
Women need to increase their calcium consumption earlier in life than men, beginning in middle age. Fulfilling the needed calcium requirement is particularly essential as a woman approaches menopause.
Women in menopause must likewise increase their calcium consumption to reduce the risk of osteoporosis and calcium shortage disease. The decrease in the hormone estrogen during menopause causes a woman’s bones to thin quicker.
The hormone condition hyperparathyroidism might also cause calcium shortage disease. Individuals with this condition don’t produce adequate parathyroid hormone, which controls calcium levels in the blood.
Other causes of calcium shortage disease include poor nutrition and malabsorption. Malabsorption is when your body can’t absorb the vitamins and minerals you require from the food you eat. Extra causes include:
- low levels of vitamin D, that makes it harder to absorb calcium
- excessive potassium, which can burn up calcium
- medications, such as those for thyroid replacement.
If you miss your daily dose of calcium, you will not become calcium deficient overnight. However it’s still essential to make an effort to obtain enough calcium every day, because the body uses it quickly. Vegans are most likely to become calcium lacking rapidly due to the fact that they don’t eat calcium-rich dairy products.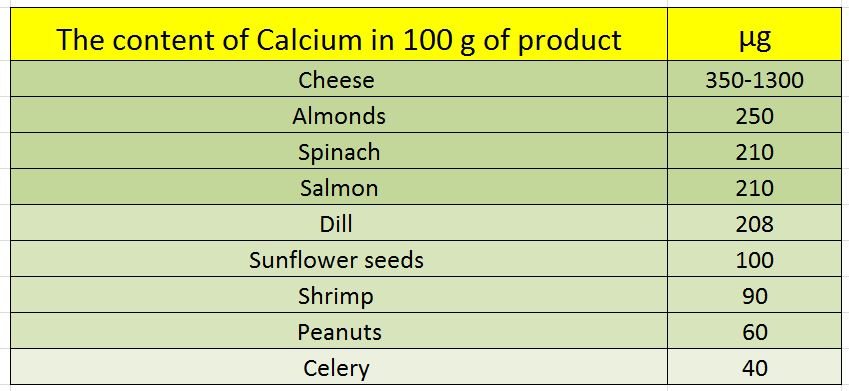
Calcium shortage won’t produce short-term symptoms because the body preserves calcium levels by taking it straight from the bones. However long-term low levels of calcium can have serious impacts.
What are the Symptoms of Calcium Deficiency Disease?
Early stage calcium deficiency may not cause any symptoms. Nevertheless, symptoms will develop as the condition progresses.
Severe symptoms of calcium deficiency disease include:
- confusion or amnesia
- muscle convulsions
- numbness and tingling in the hands, feet, and face
- depression
- hallucinations
- muscle cramps
- weak and breakable nails
- simple fracturing of the bones.
Calcium deficiencies can affect all parts of the body, leading to weak nails, slower hair growth, and delicate, thin skin.
Calcium likewise plays an essential role in both neurotransmitter release and contraction. So, calcium deficiencies can bring on seizures in otherwise healthy individuals.
If you begin experiencing neurological symptoms like amnesia, numbness and tingling, hallucinations, or seizures, make a consultation to see your doctor as quickly as possible.
How is Calcium Deficiency Disease Detected?
Contact your doctor if you have symptoms of calcium shortage disease. They’ll evaluate your medical history and ask you about family history of calcium shortage and osteoporosis.
If your doctor presumes calcium deficiency, they’ll take a blood sample to inspect your blood calcium level. Continual low calcium levels in your blood might validate a diagnosis of calcium shortage disease.
Typical calcium levels for adults can vary from 8.8 to 10.4 milligrams per deciliter, according to the Merck Manual. You might be at risk for calcium deficiency disease if your calcium level is below 8.8 mg/dL. Children and teens typically have higher blood calcium levels than adults.
Neonatal Hypocalcemia
Neonatal hypocalcemia happens in babies not long after birth. A lot of neonatal hypocalcemia happens within the first two days after birth. But late onset hypocalcemia can occur three days after birth or later on.
Risk factors for infants include being small for their age and maternal diabetes. Late start hypocalcemia is most often caused by drinking cow’s milk or formula with too much phosphate.
Symptoms of neonatal hypocalcemia include:
- jitteriness
- bad feeding
- seizures
- apnea, or slowed breathing
- tachycardia, or a faster-than-normal heart beat.
Diagnosis is made by checking a baby’s blood for the overall calcium level or ionized calcium level. The baby’s glucose level will also be tested to eliminate hypoglycemia.
Treatment usually includes providing intravenous calcium gluconate followed by numerous days of oral calcium supplements.
How is Calcium Shortage Disease Treated?
Calcium shortage is usually easy to treat. It generally includes including more calcium to your diet.
Do not self-treat by taking a great deal of calcium supplements. Taking more than the suggested dose without your doctor’s approval can lead to serious problems like kidney stones or perhaps a calcium overdose, which can be fatal.
Typically advised calcium supplements include:
- calcium carbonate, which is the least pricey and has the most essential calcium
- calcium citrate, which is the most quickly taken in
- calcium phosphate, which is likewise easily absorbed and does not cause constipation
Calcium supplements are offered in liquid, tablet, and chewable kinds.
It is essential to note that some medications could connect adversely with calcium supplements. These medications include:
- blood pressure beta-blockers like atenolol, which may increase the quantity of aluminum absorbed into the blood
- cholesterol lowering bile acid sequestrants such as colestipol, which may increase the loss of calcium in the urine
- estrogen medications, which can contribute to an increase in calcium blood levels.
Often diet changes and supplements aren’t enough to treat a calcium deficiency. In this case, your doctor may wish to manage your calcium levels by giving you routine calcium injections.
You can expect to see results within the first few weeks of treatment. Severe cases of calcium shortage disease will be monitored at one- to three-month periods.
What are the possible complications of calcium deficiency disease? Complications from calcium shortage disease include eye damage, an irregular heart beat, and osteoporosis.
Complications from osteoporosis include special needs, spine fractures or other bone fractures, and difficulty walking. If left unattended, calcium shortage disease could eventually be deadly.
How Can Calcium Shortage Disease Be Avoided?
You can prevent calcium shortage disease by including calcium in your diet every day.
Be aware that foods high in calcium, such as dairy products, can likewise be high in saturated fat and trans fat. Select low-fat or fat-free alternatives to reduce your risk of establishing high cholesterol and heart disease.
You can get one-fourth to one-third of your RDA of calcium in a single serving of some milks and yogurts.
While satisfying your calcium requirement is very important, you likewise wish to make certain you’re not getting excessive. Inning accordance with the Mayo Clinic, ceilings of calcium for adults are:
- 2,000 mg each day for males and females 51 years of age and up
- 2,500 mg each day for men and women 19 to 50 years of age.
You may want to supplement your diet by taking a multivitamin. Or your doctor might advise supplements if you’re at high risk for developing a calcium deficiency.
Multivitamins might not contain all of the calcium you need, so make certain to eat a well-rounded diet. If you’re pregnant, take a prenatal vitamin.
Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D shortage is extremely typical in the US, however lots of Americans erroneously believe they aren’t at risk since they consume vitamin-D-fortified foods (such as milk).
There are few foods that in fact have therapeutic levels of vitamin D naturally and even fortified foods do not contain adequate vitamin D to support your health requirements.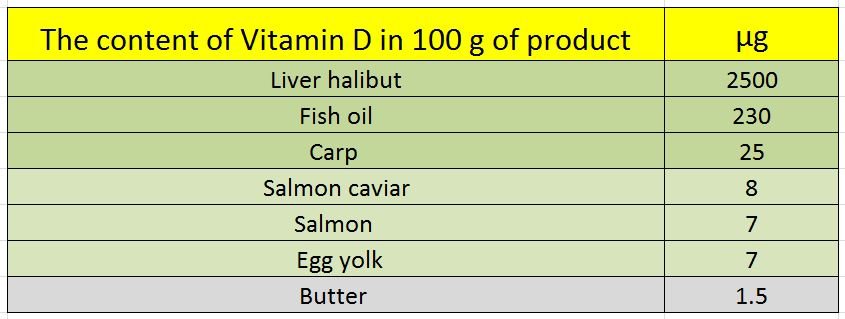
In spite of its name, vitamin D is not a regular vitamin. It’s really a steroid hormone that you are created to obtain primarily through sun direct exposure, not via your diet.
Simply How Widespread Is Vitamin D Deficiency?
Before the year 2000, few doctors ever considered the possibility that you may be vitamin D lacking.
But as the innovation to measure vitamin D ended up being economical and commonly offered, a growing number of studies were done, and it became significantly clear that vitamin D shortage was definitely rampant. For instance, according to one of the leading vitamin D scientists, Dr. Michael Holick:
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported that 32 percent of children and adults throughout the United States were vitamin D deficient– and this is grossly underestimated as they used vitamin D levels that were not constant with optimum health.
- The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that HALF of children aged one to 5 years, and 70 percent of children between the ages of 6 and 11, are deficient or inadequate in vitamin D.
- Researchers such as Dr. Holick price quote that 50 percent of the basic population is at risk of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency.
Researchers have also kept in mind that vitamin D shortage prevails in adults of all ages who always use sun defense (which obstructs vitamin D production) or restrict their outdoor activities. People with increased skin pigmentation (such as those whose ancestors are from Africa, the Middle East, or India) are also at risk, as are the senior.
It’s approximated that over 95 percent of US elderly people might be deficient in vitamin D, not just since they have the tendency to invest a lot of time indoors but likewise since they produce less in reaction to sun direct exposure (an individual over the age of 70 produces about 30 percent less vitamin D than a younger individual with the same sun direct exposure).
Signs Vitamin D Deficiency
The only method to understand for sure if you’re vitamin D lacking is by means of blood screening. Nevertheless, there are some signs and symptoms to be knowledgeable about also. If any of the following use to you, you should get your vitamin D levels checked faster rather than later on.
You Have Darker Skin
African Americans are at greater risk of vitamin D deficiency, since if you have dark skin, you may need as much as 10 times more sun exposure to produce the same quantity of vitamin D as an individual with pale skin!
As Dr. Holick discussed, your skin pigment functions as a natural sunscreen, so the more pigment you have, the more time you’ll have to spend in the sun to make appropriate amounts of vitamin D.
You Feel Depression
Serotonin, the brain hormone associated with state of mind elevation, rises with direct exposure to brilliant light and falls with decreased sun direct exposure. In 2006, researchers examined the results of vitamin D on the psychological health of 80 senior patients and discovered those with the lowest levels of vitamin D were 11 times more susceptible to be depressed than those who got healthy doses.
You’re 50 or Older
As discussed, as you grow older your skin doesn’t make as much vitamin D in action to sun direct exposure. At the same time, your kidneys become less efficient at transforming vitamin D into the type used by your body and older adults have the tendency to spend more time inside your home (i.e. getting even less sun direct exposure and for that reason vitamin D).
You’re Overweight or Obese (or Have a Higher Muscle Mass)
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble, hormone-like vitamin, which means body fat function as a “sink” by gathering it. If you’re overweight or overweight, you’re therefore likely going to require more vitamin D than a slimmer person– and the same applies for individuals with higher body weights due to muscle mass.
Your Bones Ache
Inning accordance with Dr. Holick, many who see their doctor for pains and pains, particularly in mix with tiredness, wind up being misdiagnosed as having fibromyalgia or chronic fatigue syndrome.
” Many of these symptoms are timeless signs of vitamin D deficiency osteomalacia, which is various from the vitamin D deficiency that causes osteoporosis in adults,” he states. “What’s happening is that the vitamin D shortage causes a defect in putting calcium into the collagen matrix into your skeleton. As a result, you have throbbing, hurting bone pain.”
Head Sweating
According to Dr. Holick, among the first, traditional signs of vitamin D shortage is a sweaty head. In truth, physicians used to ask brand-new moms about head sweating in their newborns for this extremely factor. Extreme sweating in newborns due to neuromuscular irritation is still referred to as a common, early symptom of vitamin D shortage.
You Have Gut Trouble
Remember, vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, which suggests if you have a gastrointestinal condition that impacts your ability to soak up fat, you may have lower absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin D too. This includes gut conditions like Crohn’s, celiac and non-celiac gluten level of sensitivity, and inflammatory bowel disease.
How Much Vitamin D Do You Need for Ideal Health?
When it concerns vitamin D, you do not wish to remain in the “typical” or “normal” range, you wish to remain in the “optimal” variety. The factor for this is that as the years have passed, researchers have gradually moved that range up. At present, based on the examination of healthy populations that get plenty of natural sun exposure, the optimal range for basic health seems someplace between 50 and 70 ng/ml.
When it comes to how to optimize your vitamin D levels, I securely believe that suitable sun exposure is the best way.
Typically speaking, this will be when your skin turns the lightest shade of pink or, as Dr. Holick recommends, about half of the time you think it would take you to obtain a mild sunburn (So if you understand you have the tendency to get sunburned after 30 minutes, you ‘d want to stay in the sun for about 15 minutes).
If your situations don’t give you to access the sun, then you actually just have one choice if you wish to raise your vitamin D, which is to take a vitamin D supplement. As a general standard, research by GrassrootsHealth recommends that adults require about 8,000 IUs daily to accomplish a serum level of 40 ng/ml. If you do go with a vitamin D supplement, please remember that you likewise have to enhance your consumption of vitamin K2 through food and/or a supplement.
If you’re getting your vitamin D from the sun, this is not as crucial, although you ‘d be smart to make certain you’re getting adequate quantities of vitamin K2 from your diet either way.
Vitamin D Foods Sources
Vitamin D is essential since it increases the rate calcium is soaked up into your blood. Ask your doctor how much vitamin D you need.
To increase your calcium intake, you can include food abundant in vitamin D to your diet. These include:
- fatty fish like salmon and tuna
- strengthened orange juice
- strengthened milk
- portobello mushrooms
- eggs.
Just like calcium-rich dairy products, some vitamin D-rich dairy products can likewise be high in hydrogenated fat.
Health Tips
In addition to maintaining healthy calcium and vitamin D levels, there are specific lifestyle changes you can make to promote bone health. These include preserving a healthy body weight, exercising regularly, and don’t consume alcohol (alcohol is harmful for health) and don’t smoke.
About the Author
Reyus Mammadli is the author of this health blog since 2008. With a background in medical and biotechnical devices, he has over 15 years of experience working with medical literature and expert guidelines from WHO, CDC, Mayo Clinic, and others. His goal is to present clear, accurate health information for everyday readers — not as a substitute for medical advice.






